肿瘤相关抗原(Tumor-associated antigens,TAA)是指在肿瘤细胞特有或高表达,而在健康细胞上不存在或低表达的抗原分子,参与肿瘤细胞的增殖、分化和迁移,这使得TAA成为潜在的抗肿瘤药物有效分子靶点。TAA靶点相关药物能够通过介导ADCC、CDC、激活免疫反应等作用杀伤肿瘤细胞。针对该类型药物,可使用野生型小鼠皮下接种/原位接种经过人源化改造的鼠源细胞系进行药效评价。
百奥赛图根据目前TAA靶点药物研发市场需求,开发了一系列人源化细胞系,可用于药效评价。
部分TAA靶点在健康组织和细胞中表达,并发挥重要的生理功能,针对这类靶点的药物可能发生严重的毒副作用,百奥赛图可提供相应人源化动物模型,进行药物的安全性评价。
310705 |
B-hB7-H3 EL4 |
310708 |
B-hEPCAM MC38 |
310704 |
B-hB7-H3 MC38 |
310825 |
B-hFAP MC38 |
310720 |
B-hBCMA MC38 |
310724 |
B-hHER2 EL4 |
310712 |
B-hCD19 EL4 |
311147 |
B-hHLA-E MC38 |
310706 |
B-hCD19 MC38 |
310693 |
B-hHVEM MC38 |
310717 |
B-hCD20 EL4 |
310815 |
B-hLILRB4 MC38 |
310716 |
B-hCD20 MC38 |
311600 |
B-hMERTK MC38 |
310976 |
B-hCD37 MC38 |
320714 |
B-hPD-L1 plus/hCD47 MC38 |
310695 |
B-hCD47 MC38 |
320722 |
B-hPD-L1 plus/hCEA MC38 |
310690 |
B-hCEACAM1 MC38 |
310703 |
B-hPD-L2 MC38 |
310791 |
B-hCLDN18.2 A549 |
310807 |
B-hROR1 MC38 |
310715 |
B-hCLDN18.2 MC38 |
311082 |
B-hTF MC38 |
310824 |
B-hCXCR2 MC38 |
311068 |
B-hTPBG MC38 |
310896 |
B-hCXCR4 MC38 |
310702 |
B-hCD47 CT26.WT |
310713 |
B-hEPCAM EL4 |
310696 |
B-hCD47 MC38 |
靶点人源化小鼠是指将药物靶点或疾病相关的人源蛋白敲入并破坏鼠同源蛋白的动物模型。该小鼠模型具有功能健全的免疫系统,可用于免疫治疗的药效评价;同时,由于使用人源蛋白替换了鼠同源蛋白,克服了部分抗体不能人鼠交叉识别的问题,可使用人源或人源化抗体药物进行药效评价,解决了以往只能使用替代抗小鼠抗体进行药效评价的难点,在提高药物研发转化率的同时,极大降低了研发成本。此外,相比于免疫缺陷鼠人免疫重建模型,具有更高的成本效益和结果稳定性。
百奥赛图根据目前新药研发市场需求,开发了一系列单靶点/双靶点或多靶点人源化小鼠模型,并根据可能的药物作用机理,开发了相应的人源化肿瘤细胞系,以提供更加完善和有效的药效评价疾病模型。
目前可提供服务的人源化小鼠模型主要包括免疫检查点人源化、细胞因子人源化、GPCR人源化和其他人源化小鼠,详细信息可在人源化动物模型部分查看。
模型数据展示

Gene description
TNFRSF9 (Tumor necrosis factor receptor super family, member 9), also called CD137 and 4-1BB, is a co-stimulatory molecule and is mainly expressed on the surface of T, B, NK and mononuclear cells. CD137 is activated by its ligand CD137L or activating anti-CD137 antibodies enhance tumor rejection because it is upregulated on T cells following activation and its engagement increases T cell proliferation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. The clinical development of 4-1BB targeting therapy was slow due to the toxicity associated with overt immune activation. Fortunately, new therapeutic modalities using 4-1BB targeting aptamers as well as therapeutic combinations with other immuno-modulatory and traditional anti-cancer treatments have revived excitement for the use of 4-1BB agonists in the clinical.
Protein expression analysis
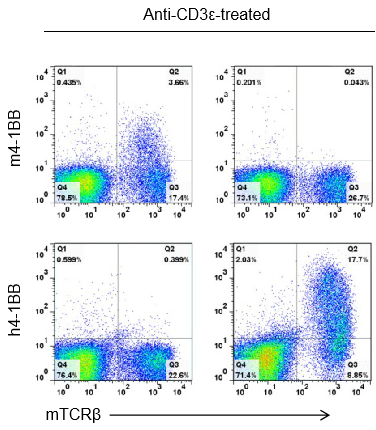
Strain specific 4-1BB protein expression analysis in wild-type (+/+) or homozygous B-h4-1BB (H/H) mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from +/+ and homozygous mice stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-4-1BB antibodies. Mouse 4-1BB was detectable in +/+ mice, while human 4-1BB was exclusively detectable in B-h4-1BB H/H mice.
High dose of urelumab resulted in liver toxicity in B-h4-1BB mice
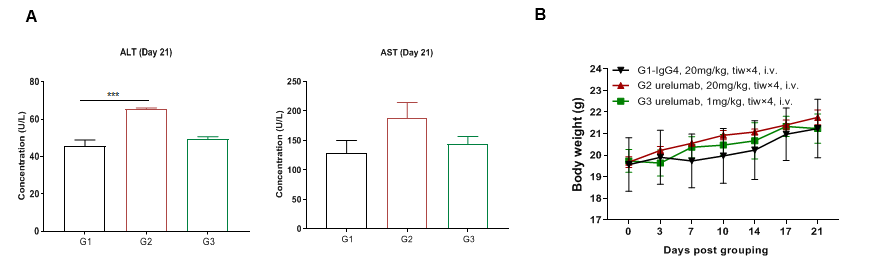
High dose of urelumab therapy resulted in increased lymphocyte infiltration in liver in B-h4-1BB mice
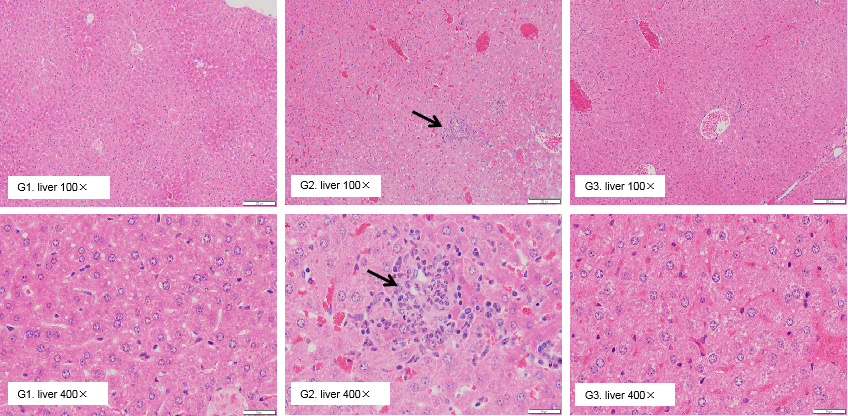
Pathological analysis of liver toxicity. Chronic inflammation (arrow) was observed in the liver of B-h4-1BB mice which were treated with high dose (20mg/kg) of urelumab (in house) for 21 days. While there were no microscopic changes in groups G1 and G3 which respectively treated with low dose (1mg/kg) of urelumab (in house) and high dose (20mg/kg) of Isotype.
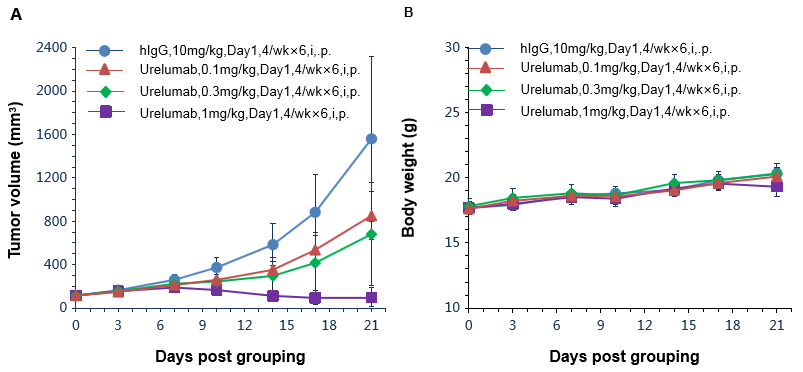
Antitumor activity of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies in B-h4-1BB mice. (A) Anti-human 4-1BB antibodies inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (female, 6-7 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human 4-1BB antibody urelumab (in house) with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human 4-1BB antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice, demonstrating that the B-h4-1BB mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn