
Background
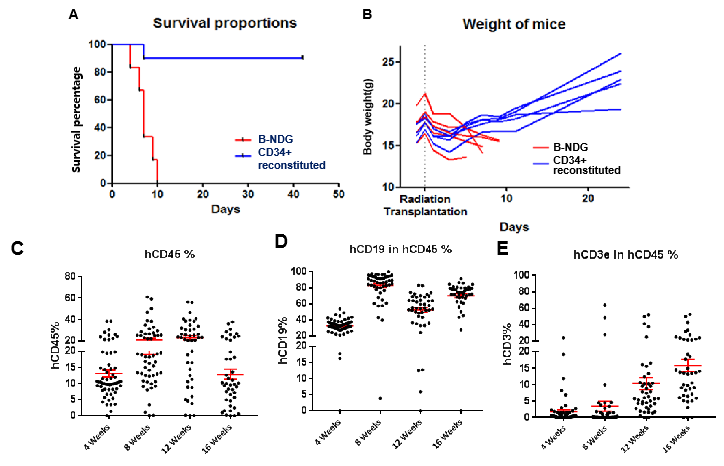
The Immune-deficient B-NDG mouse model (NOD.CB17-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1/Bcgen) was independently designed and generated by Biocytogen. B-NDG mice are generated by deleting the IL2rg gene from NOD-scid mice with severe immunodeficiency phenotype. Lacking mature T cells, B cells or functional NK cells, and displaying cytokine signaling deficiencies , this mouse model has the highest degree of immunodeficiency and thus is most suitable for engraft and growth of human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and human tumor cells or tissues.
• NOD-scid (non-obese diabetes, severe combined immunodeficiency) genetic background: mice of NOD genetic background and with Prkdc (protein kinase DNA-activated catalytic) knockout. Functional T cells, B cells and complement system in these mice are lost, and the activity of NK cells is greatly weakened.
• IL2rg null: the gamma chain of Interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R γc, also called CD132) is on the mouse X chromosome, and is the common receptor subunit of cytokines IL2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and IL-21 with important immune functions. After IL2r is knocked out, mouse immunity function is greatly weakened, activities of NK cells, which are almost completely lost.
• Prkdc null (DNAPK, scid): Prkdc (protein kinase DNA-activated catalytic) null mutation is characterized by significantly deficient of functional T cells and B cells, and an absence of lymphocytes, recapitulating severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) in human patients.
Major Applications
• Human-derived cell or tissue engraftment
• Tumor and tumor stem cell research
• ES and iPS cell research
• Hematopoiesis and immunology studies
• Human infectious disease studies
• Development of humanized models

Animal breeding and maintenance
B-NDG mice are housed in isolators instead of IVCs in our facility. Based on our experience, the mice can live up to 2 months in SPF standard IVCs. This time frame matches the requirements of most experiments performed with B-NDG mice. To improve facility standards, strict sanitation procedures are recommended: cages and bedding need to be sterilized by autoclaving or Co60 irradiation before use, and cages need to be changed in laminar flow hoods weekly. Keeping a clean, high standard housing environment helps to improve the life span of B-NDG mice.
Animal husbandry

Animal breeding and maintenance
Transportation
Biocytogen’s B-NDG mouse can be shipped using land and/or air. Although the courier is notified to handle the crate with care, stress response of mice during shipment is still inevitable. Although enough supply of water jelly and food will be provided in cages, increased metabolism and fecal excretion caused by the stress may result in dehydration and loss of body weight. General percentage weight loss due to shipment is ~10%. The percentage can be as high as 15% if the shipment procedure is longer and the cage is populated. Usually, the most of the lost body weight is regained (although cannot reach 100%) after 5-7 days of adaptive feeding (Labdiet food is recommended)).
Adaptive feeding
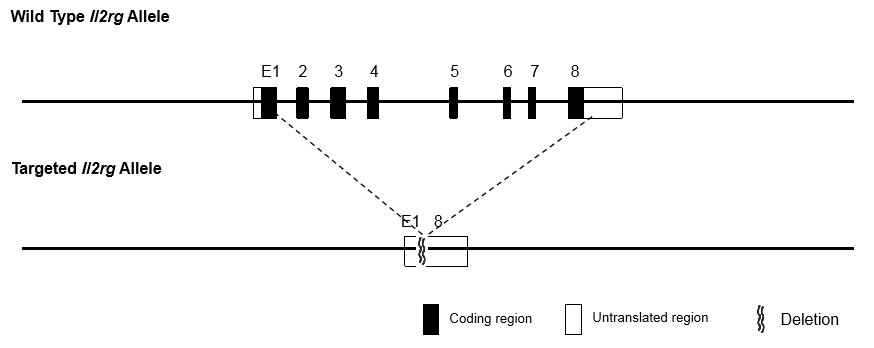
Generation of gene editing mouse model
Phenotypic analysis
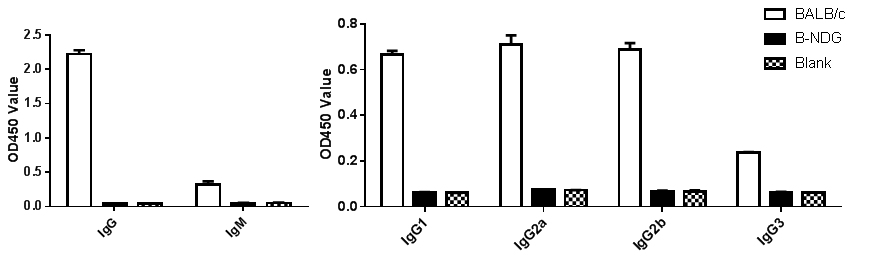
Body weight growth

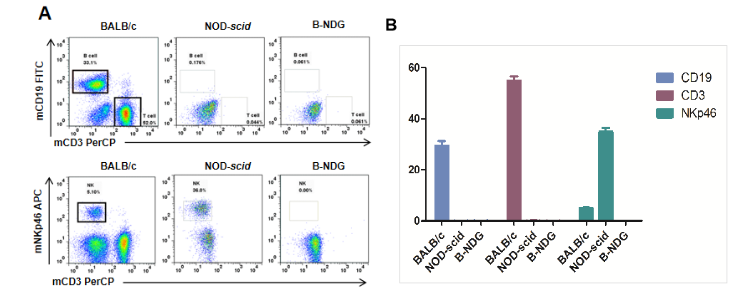
Flow-cytometric Analysis Using Specific Markers for T, B and NK Cells
Histology of spleen from B-NDG mice
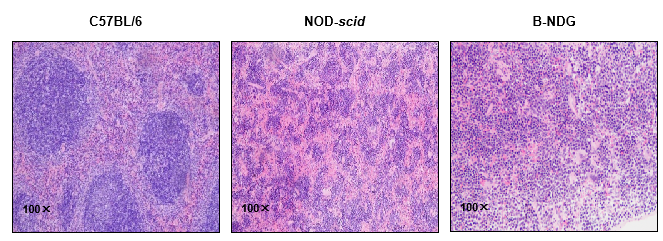
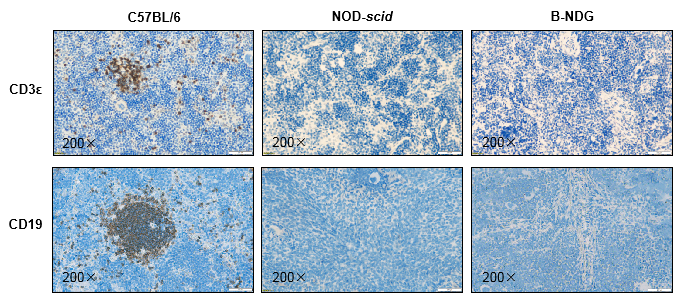
Figure 5. Histological sections of spleen from 9-week-old C57BL/6, NOD-scid, and B-NDG mice (n=3).
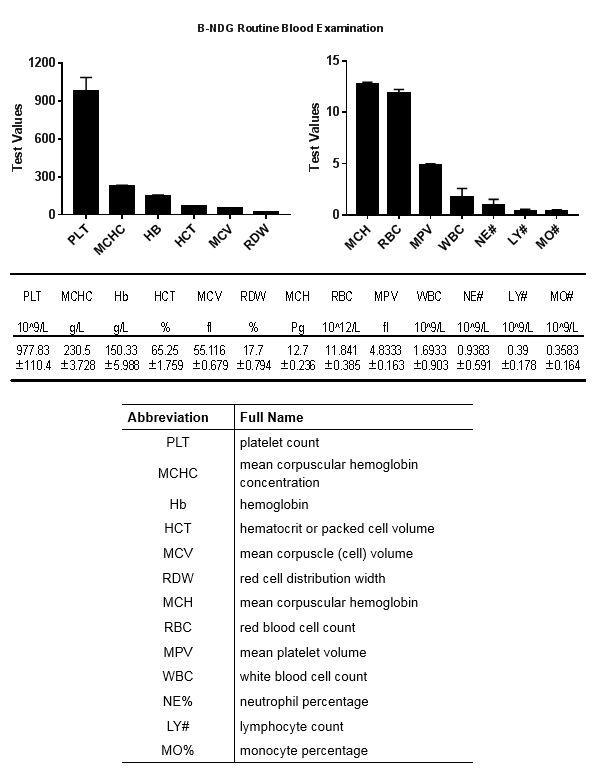
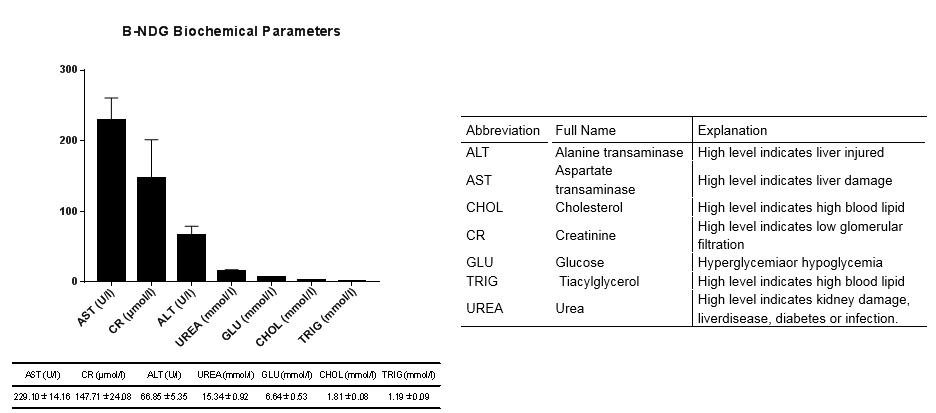
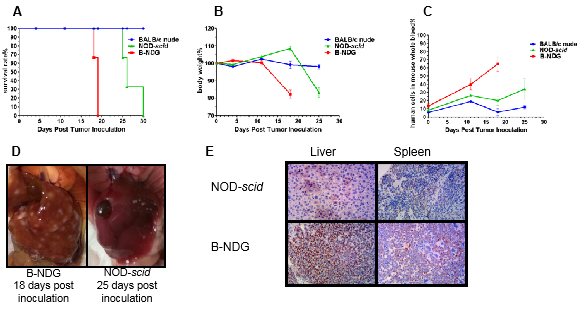
Figure 8. Raji B cells (5X106) were injected in to each B-NDG, NOD-scid and BALB/C Nude mice.
Drug in vivo efficacy study using Raji lymphoma CDX Tumor metastasis model in B-NDG mice.
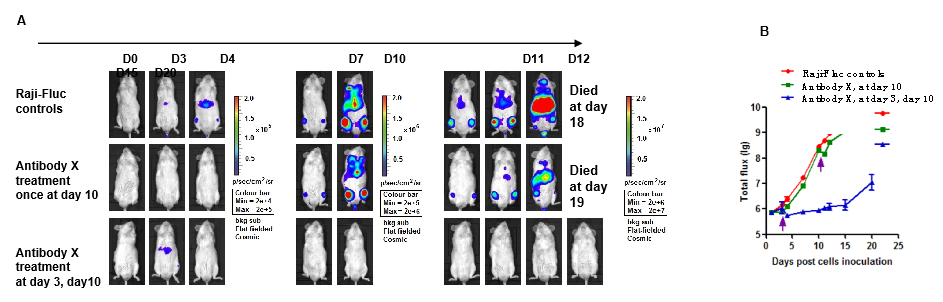
Figure 9. Raji-Fluc cells (5×105) were injected into B-NDG mice and the same dose of antibody X was given at day 3 and day 10. (A) In vivo imaging recorded at different time points to observe disease progression in mice. (B) Tumor curve for tumor cell fluorescence curves in different groups of mice. The effect of early treatment (at day 3, day 10) is remarkable, and this effect is significantly reduced for the late treatment (at day 10).
Human CD47 antibody in vivo efficacy study using Raji lymphoma CDX Tumor model in B-NDG mice.
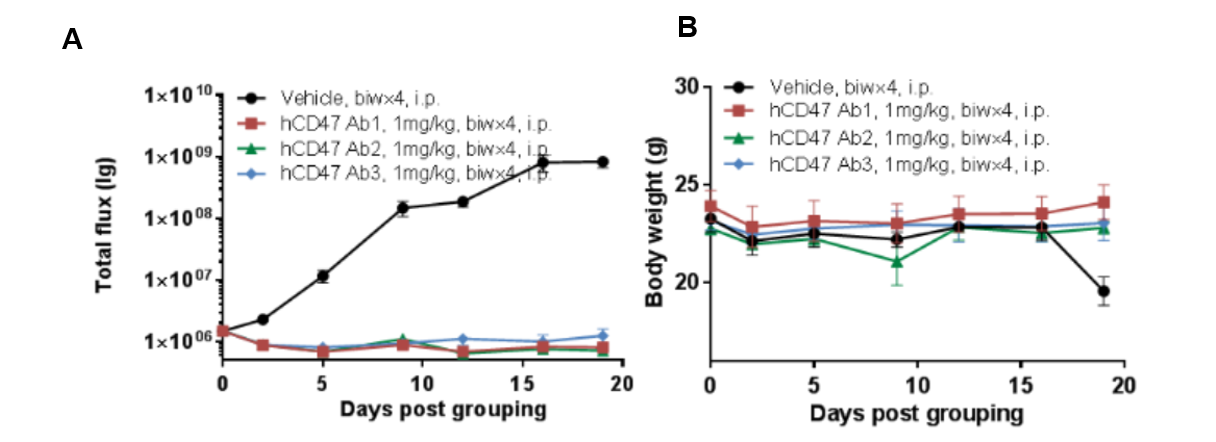
Human B-luciferase-GFP Raji cells (B lymphocytes) were caudal vein implanted into B-NDG. Mice were grouped when the fluorescence intensity reached approximately 1.0E+06 (n=6) at which time they were treated with anti-human CD47 antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel A. (A) fluorescence imager was used to monitor tumor fluorescence in mice. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. The results showed that 3 antibodies had efficacies for tumor growth inhibition in B-NDG mice. B-NDG is a powerful model for human CD47 antibody efficacy study. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
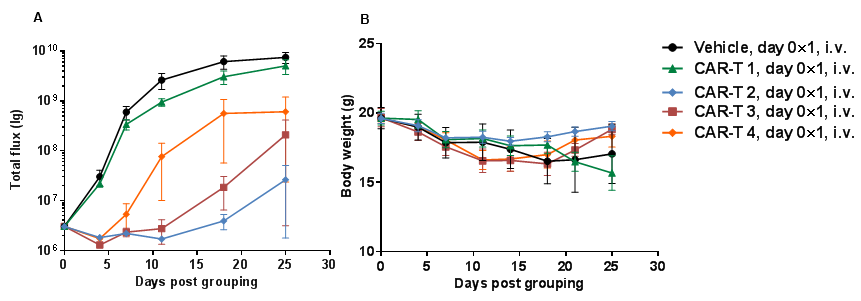
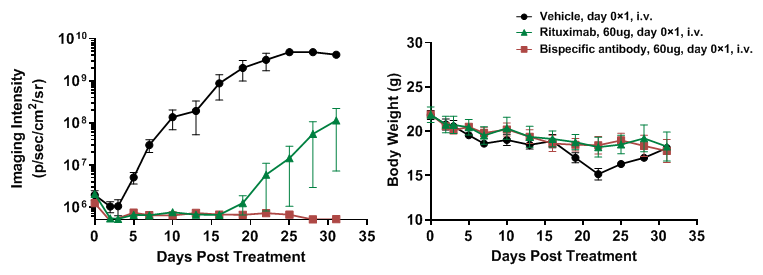
Human B-luciferase-GFP Raji cells (5E5), PBMC (5E6) and antibodies mixture were intravenously injected into B-NDG mice (n=4). (A) fluorescence imager was used to monitor tumor fluorescence in mice. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. Bispecific antibody shows significant inhibitory effects. The results indicate that establishing a CDX tumor model in B-NDG mice with reconstituted PBMCs provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Human Immune System Reconstituted Models and Efficacy Evaluation
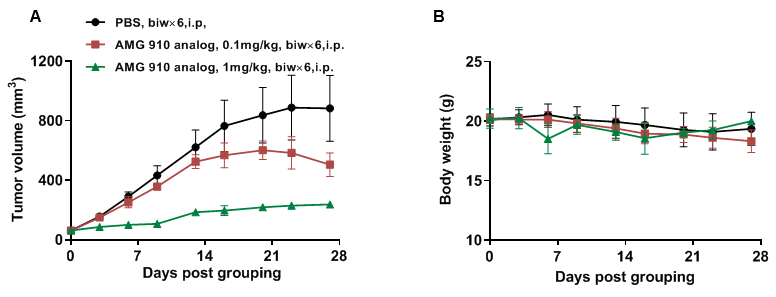
Figure 20. B-NDG mice reconstituted with PBMCs cells were used for CD3×Claudin18.2 bispecific antibody efficacy studies
NUGC4 cells (5E6) were subcutaneously implanted after human PBMCs (5E6) were intravenous implanted into B-NDG mice (female, 7 week-old, n=6). The animals were grouped into control and treatment when the tumor size was approximately 50-80 mm3 and the percentage of human blood hCD45% were above 10%, at which time they were treated with drugs. (A) Anti human CD3×Claudin18.2 bispecific antibody (AMG 910 analog) inhibited NUGC4 tumor growth in human PBMC reconstituted B-NDG mice. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. CD3×Claudin18.2 bispecific antibody shows significant tumor inhibitory effects. The results indicate that establishing a CDX tumor model in B-NDG mice with reconstituted PBMCs provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
近年来,免疫检查点抑制剂在肿瘤治疗中取得突破性进展,在多种实体瘤中均取得了较好的治疗效果,免疫治疗因而备受关注。百奥赛图B-NDG小鼠表现为缺乏成熟的T、B、NK细胞,是目前国际公认的免疫缺陷程度高、适合人源细胞或组织移植的工具小鼠。但由于模型本身免疫系统的缺陷,无法进行免疫治疗的药效评价。对免疫缺陷鼠进行人免疫系统重建,能够很好的解决这一问题:将人的免疫细胞、造血干细胞移植到B-NDG及B-NDG衍生小鼠中构建的免疫系统重建小鼠,能够更好的模拟人的免疫系统,进行免疫学研究和免疫药物评价。
根据人免疫系统重建移植的细胞类型,百奥赛图目前可提供三类免疫重建模型:人外周血单核细胞(PBMC)重建,人造血干细胞(CD34+ HSC)重建和NK细胞重建。利用免疫重建小鼠模型,能够进行肿瘤免疫治疗药物的药效评价,为新药研发及临床前评估提供有力支持。
B-NDG mice 免疫重建模型+CDX
在人PBMC重建的B-NDG小鼠中进行单抗和双特异性抗体抗CDX肿瘤药效研究
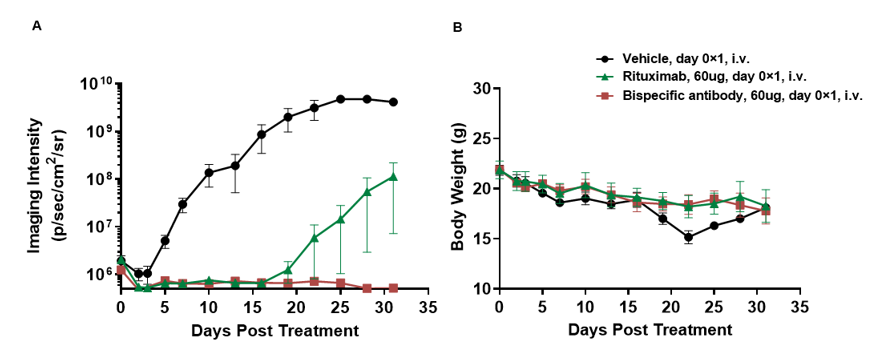
将人 B-luc-GFP Raji(5E5)、PBMC (5E6) 和抗体混合物静脉注射到 B-NDG 小鼠 (n = 4) 中。(A) 小动物成像仪监测小鼠肿瘤荧光。(B) 治疗期间的体重变化。单抗表现出明显的抑瘤效果,双特异性抗体的抑制作用更加显著。结果表明,使用 PBMC重建的B-NDG小鼠建立CDX肿瘤模型为体内评价抗体提供了有力的临床前模型。数值表示为平均值±SEM。
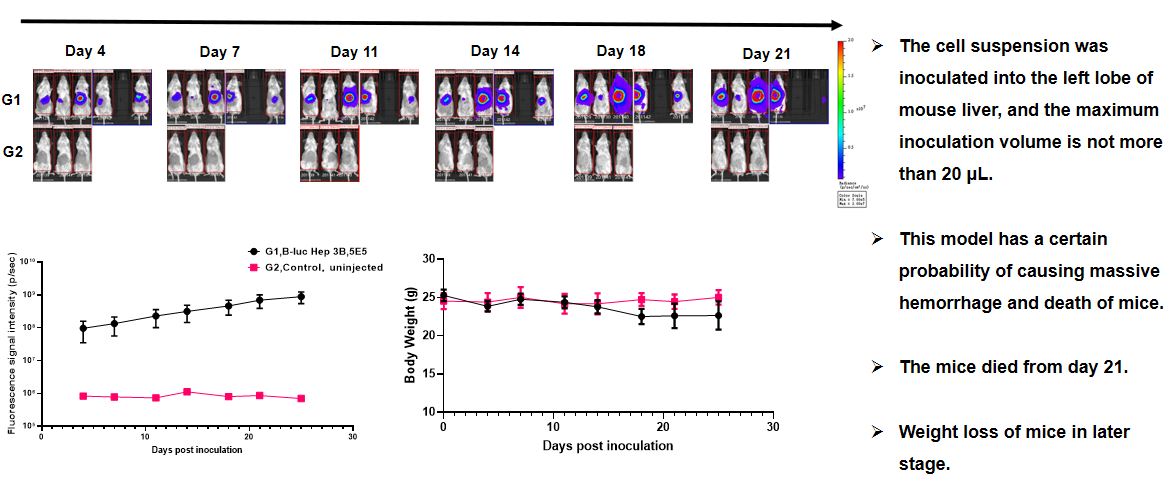
原位瘤和转移瘤模型汇总
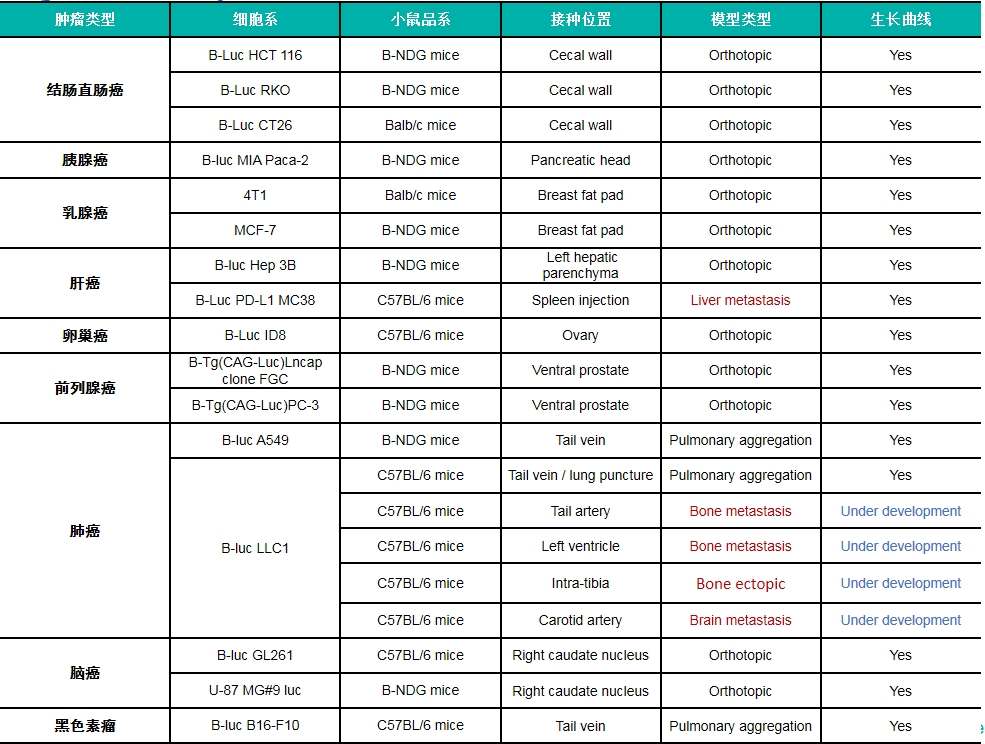
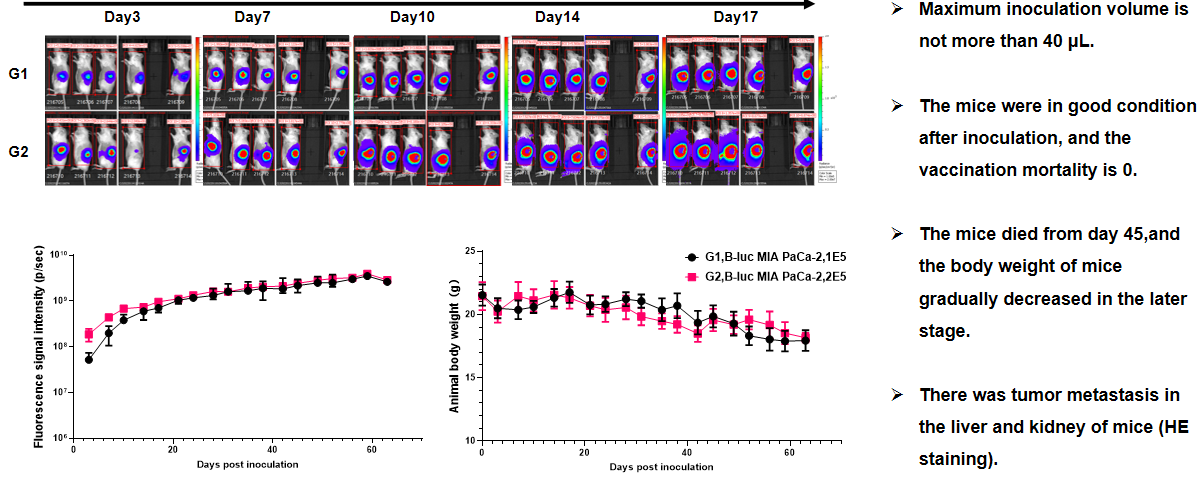
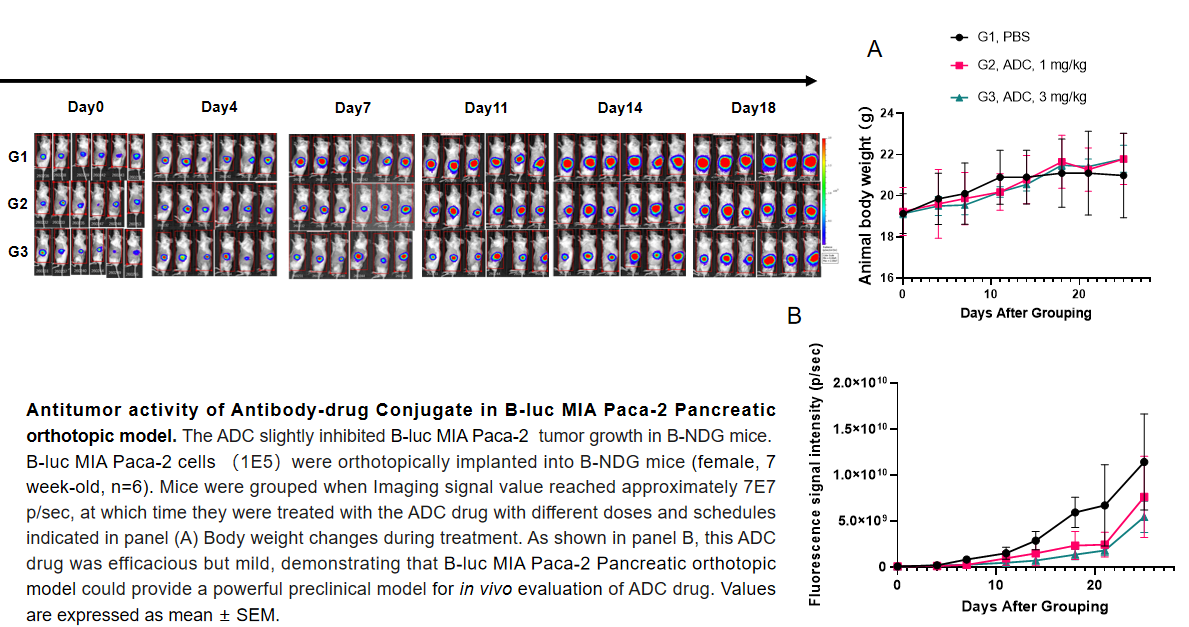
Pancreatic cancer:B-luc MIA Paca-2 #4+ B-NDG mice(orthotopic)
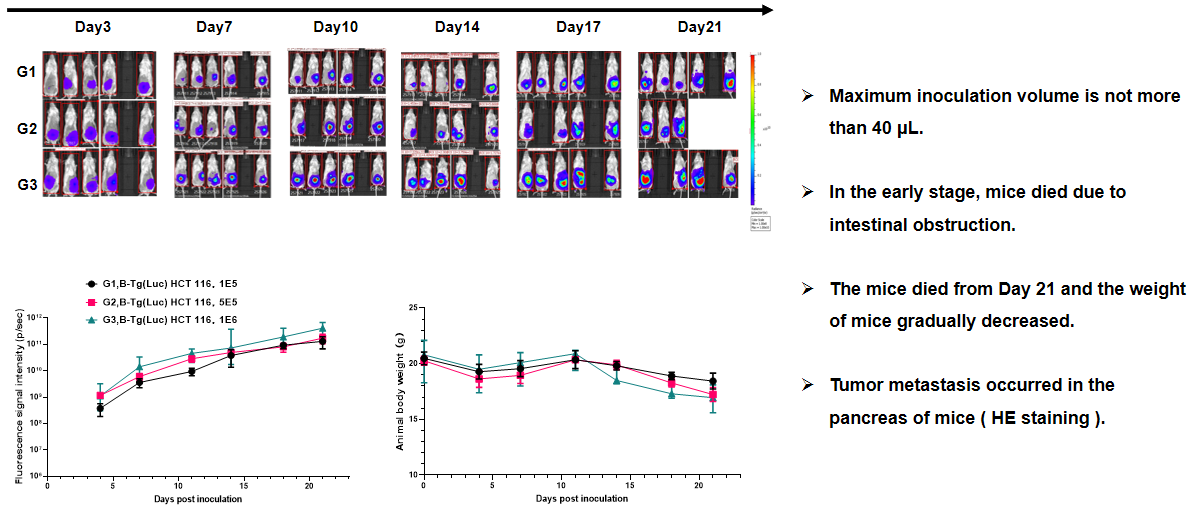
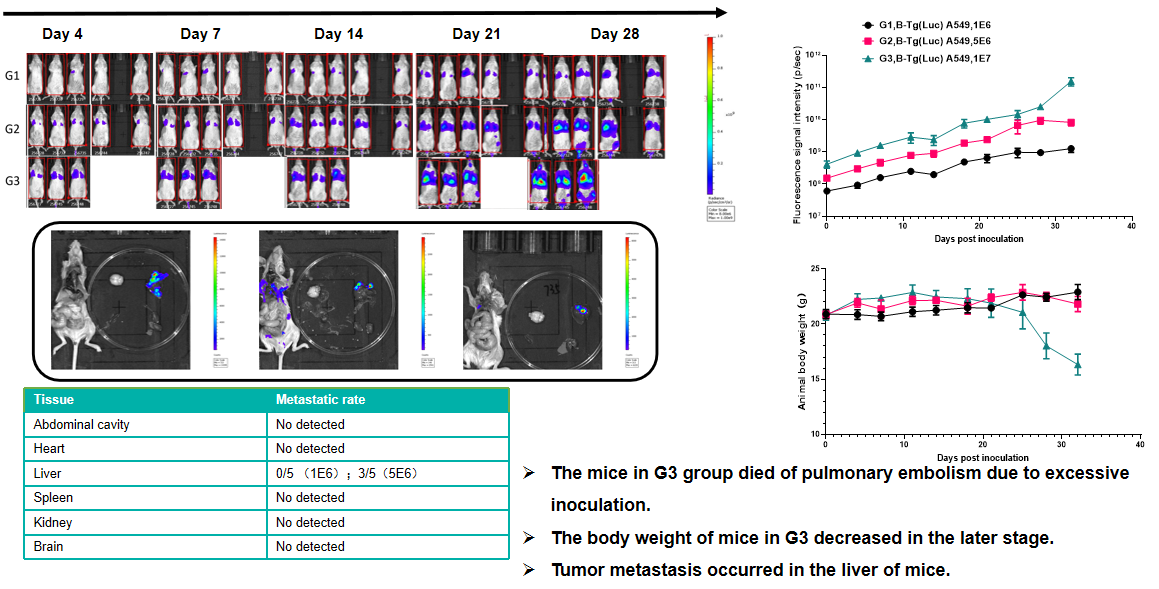
Lung cancer:B-Tg(Luc) A549(mix)+ B-NDG mice( i.v.)
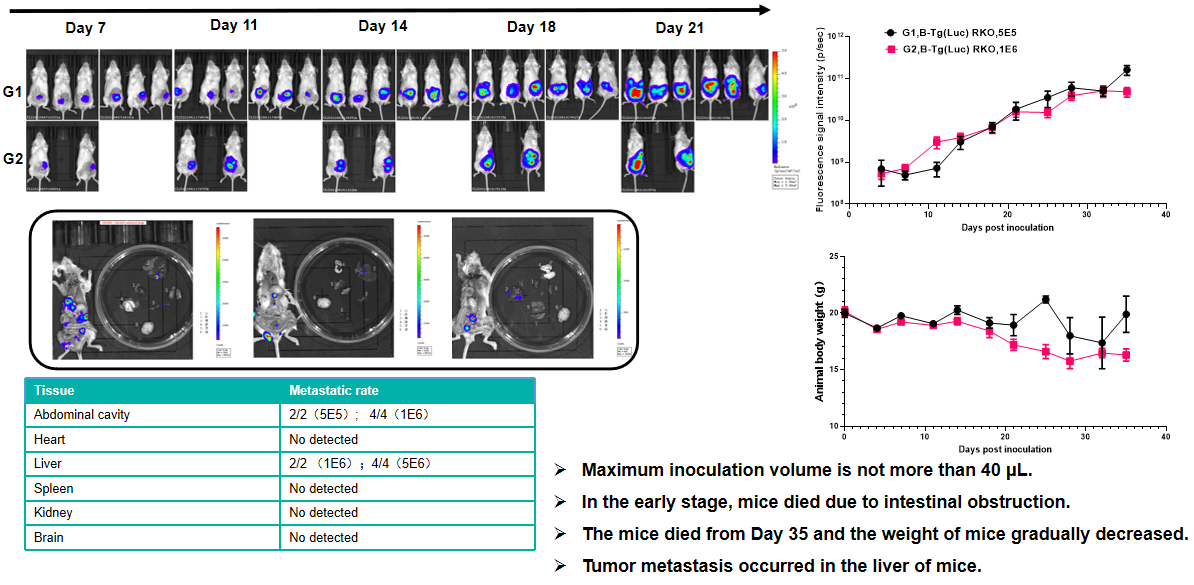
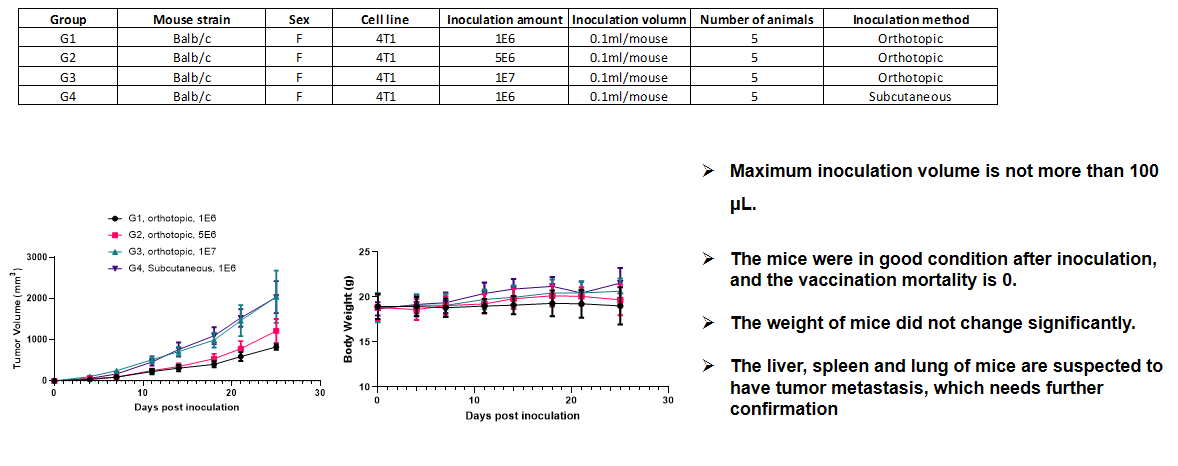
Breast cancer:4T1+ Balb/c mice(orthotopic)
在B-NDG小鼠中成功建立PDX模型
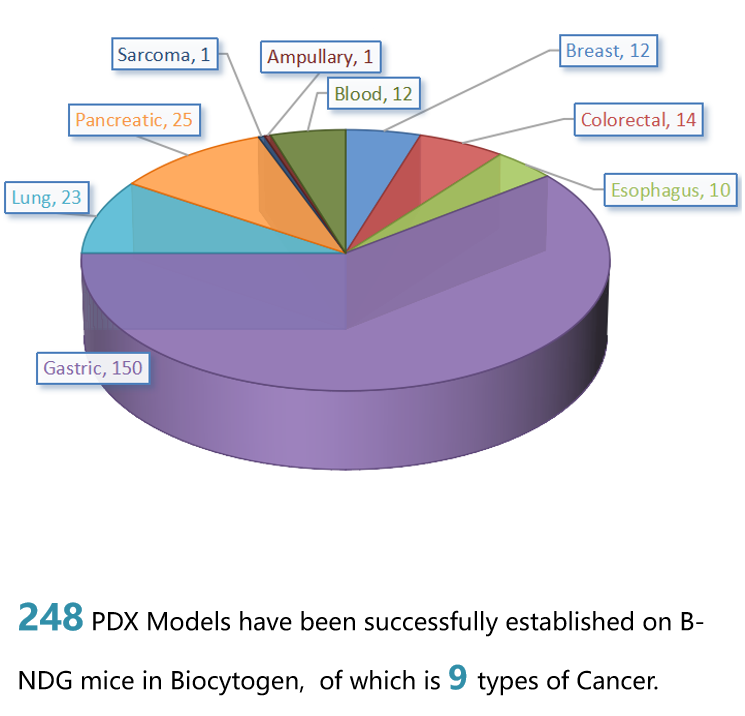
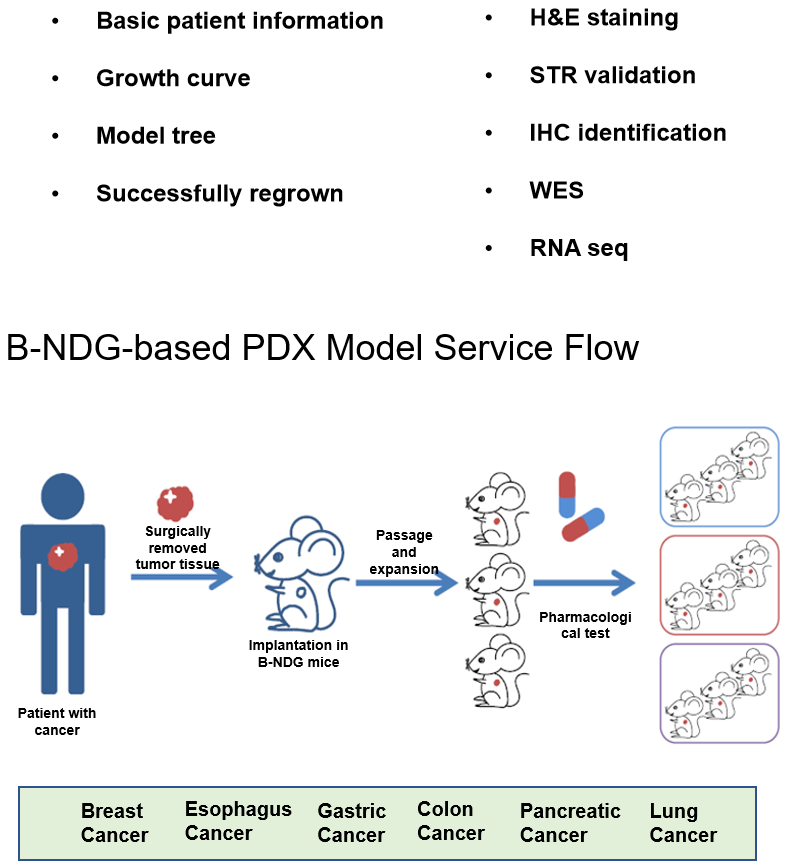
PDX模型中供试品的疗效评估
1、实体瘤PDX
案例:胰腺癌—BP0062
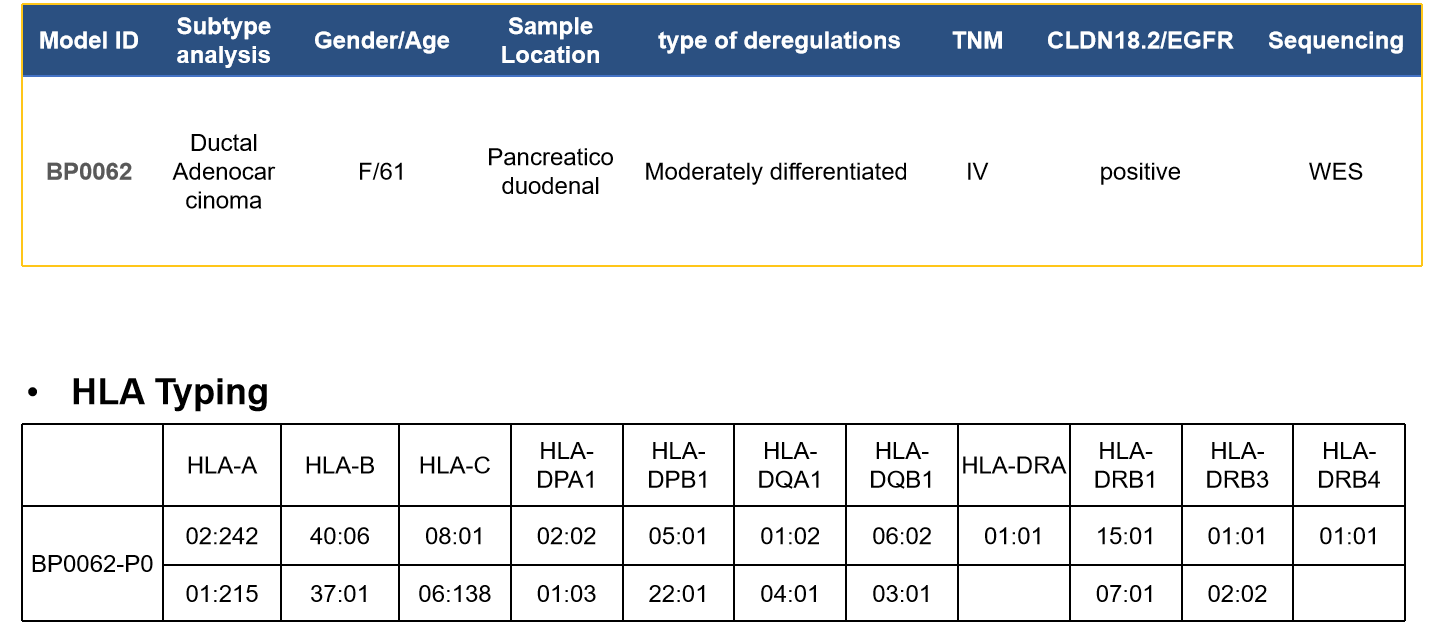
- 不同代次B-NDG小鼠的生长曲线
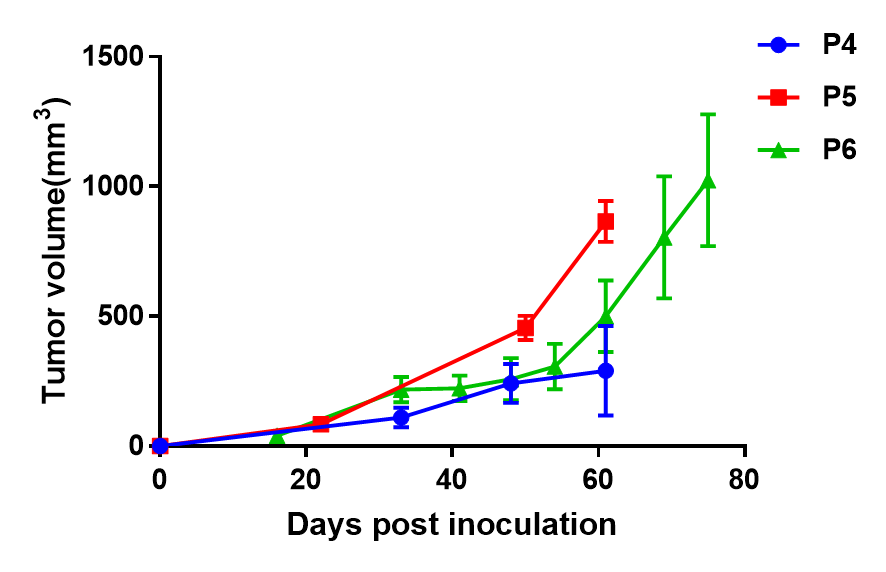
将BP0062植入B-NDG小鼠皮下。体积以mm3表示,公式V=0.5a X b2,其中a、b分别为肿瘤长径和短径。肿瘤平均体积±SEM。
结果:胰腺癌BP0062 PDX模型能够在B-NDG小鼠中稳定建立肿瘤模型,并能有效跟踪肿瘤体积。
- 模型验证
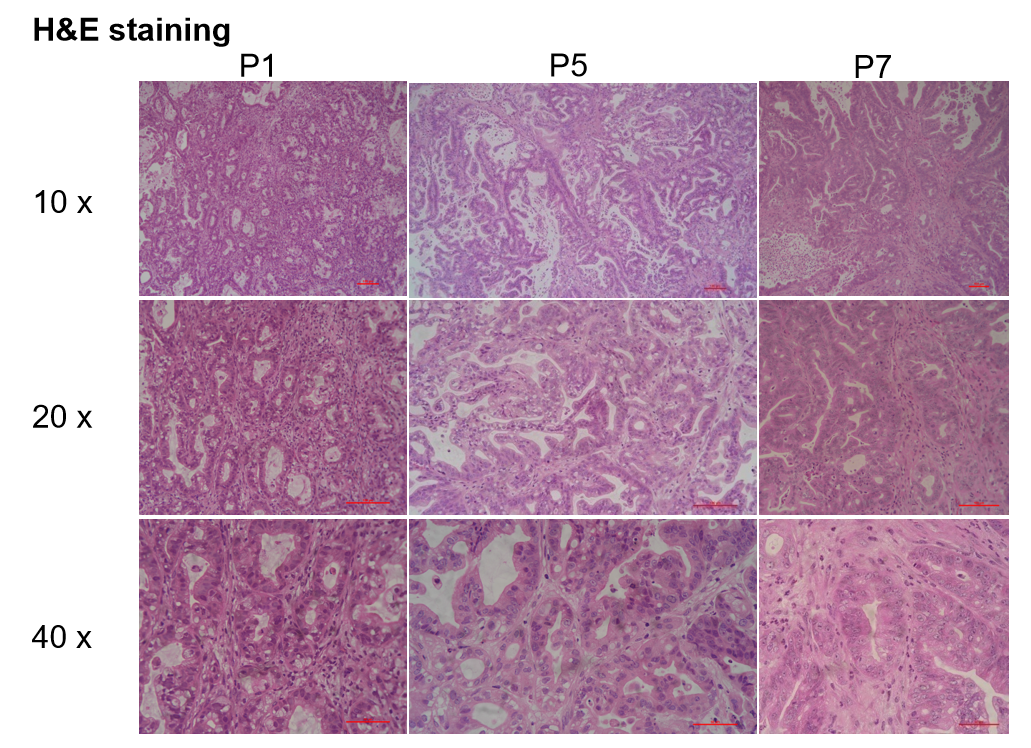
Patient-derived xenografts were found to recapitulate the structures in original patient samples and maintain similar heterogeneity in different generations. 患者来源的异种移植物被发现重现了原始患者样本中的结构,并在不同代中保持了相似的异质性。
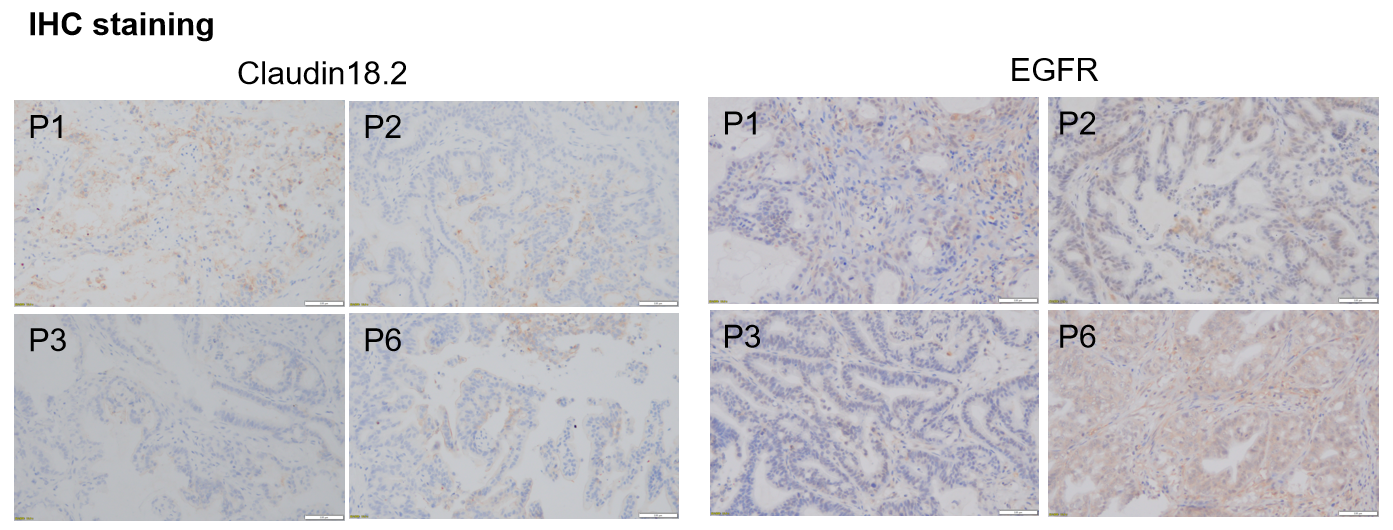
对CLDN18.2和EGFR的全面免疫组化评估显示,不同代的个体肿瘤之间没有明显的异质性。
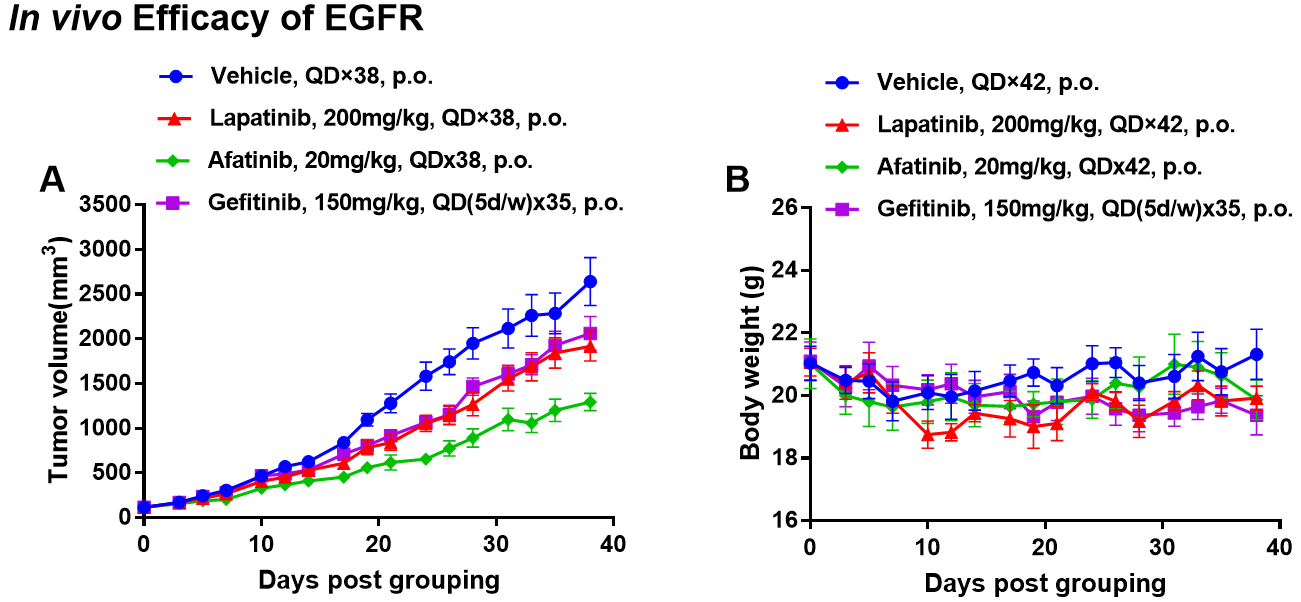
靶向EGFR的药物在B-NDG小鼠中的抗肿瘤活性。(A)分子靶向小分子抗癌药物轻度抑制BP0062在B-NDG小鼠体内的肿瘤生长。将BP0062的PDX模型植入B-NDG小鼠(雌性,6周龄,n=6)皮下。当肿瘤体积达到约100 mm3时对小鼠进行分组,在这个时间点,小鼠接受不同的靶向药物治疗,治疗期间的体重变化见图(B)。如图A所示,分子靶向小分子抗癌药物疗效显著,表明BP0062的PDX模型可用于建立肿瘤模型,为EGFR阳性细胞提供了一种强大的临床前胰腺肿瘤模型。值表示为平均值±SEM。
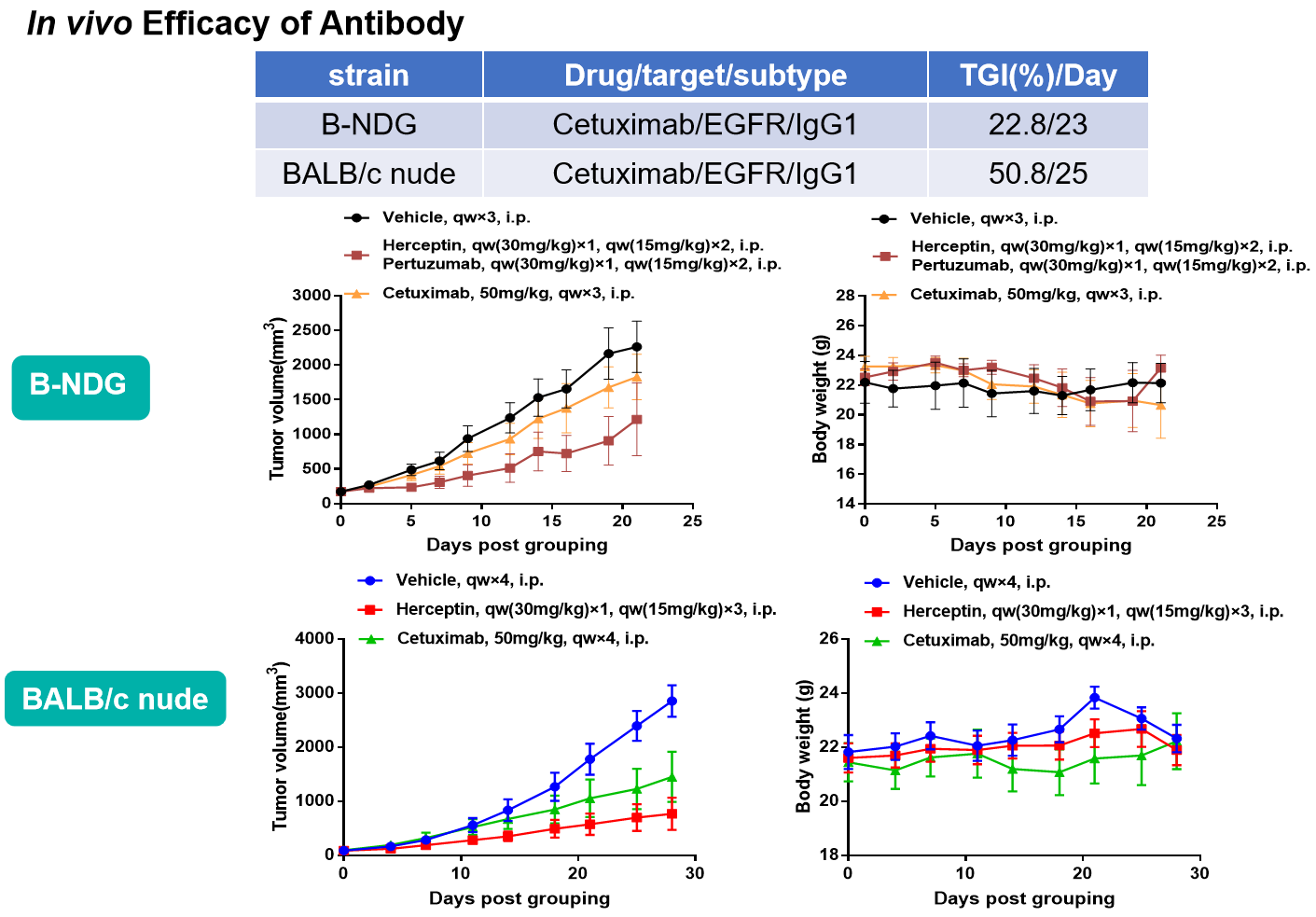
- 不同品系小鼠在相同PDX模型中的反应
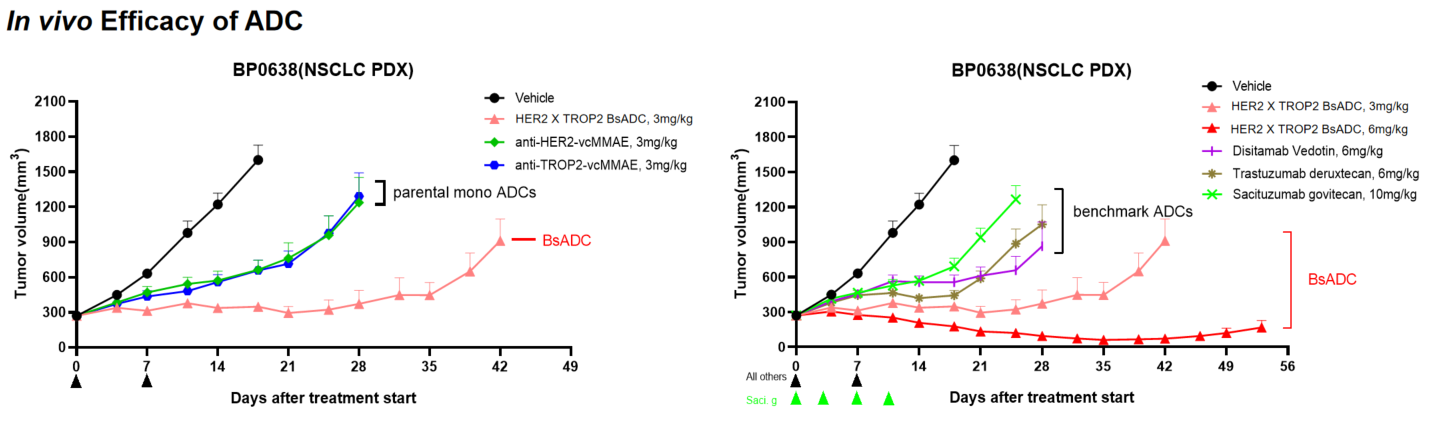
- 体内药效:HER2 X TROP2 BsADC在HER2低的PDX模型中显示出强大的抗肿瘤活性

2、血液瘤PDX
案例:白血病 PDX—BP2010
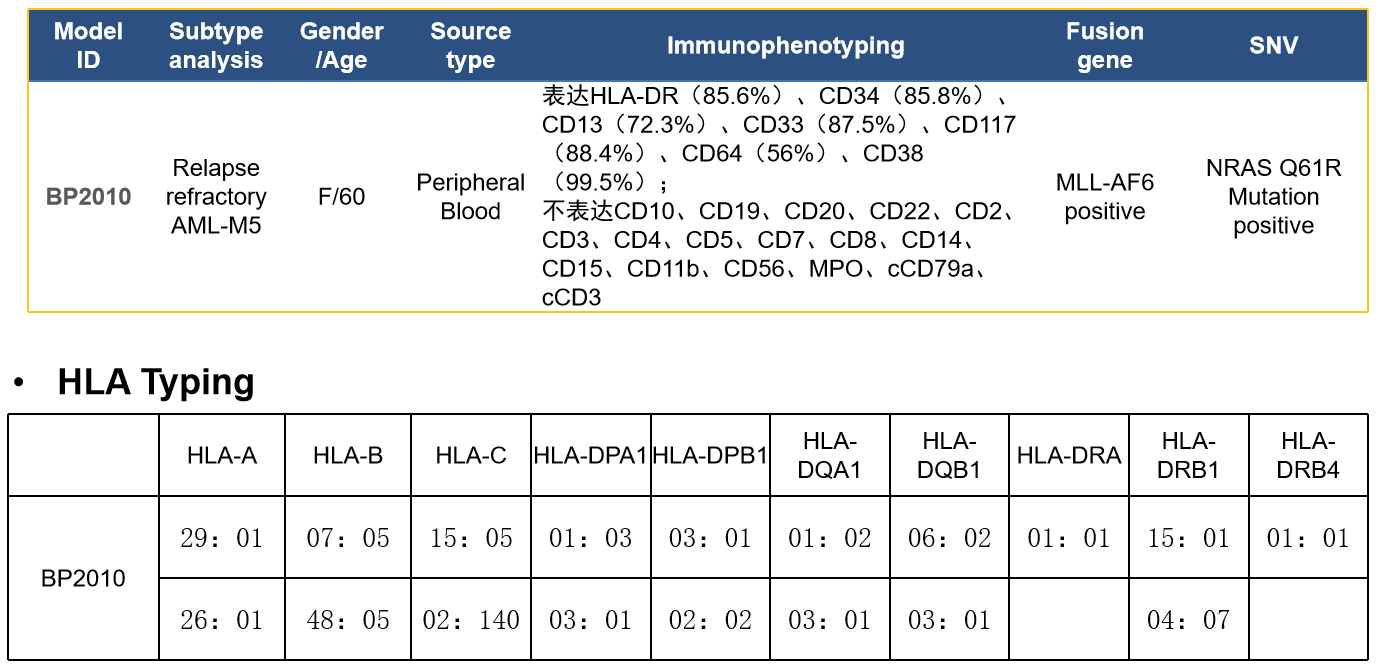
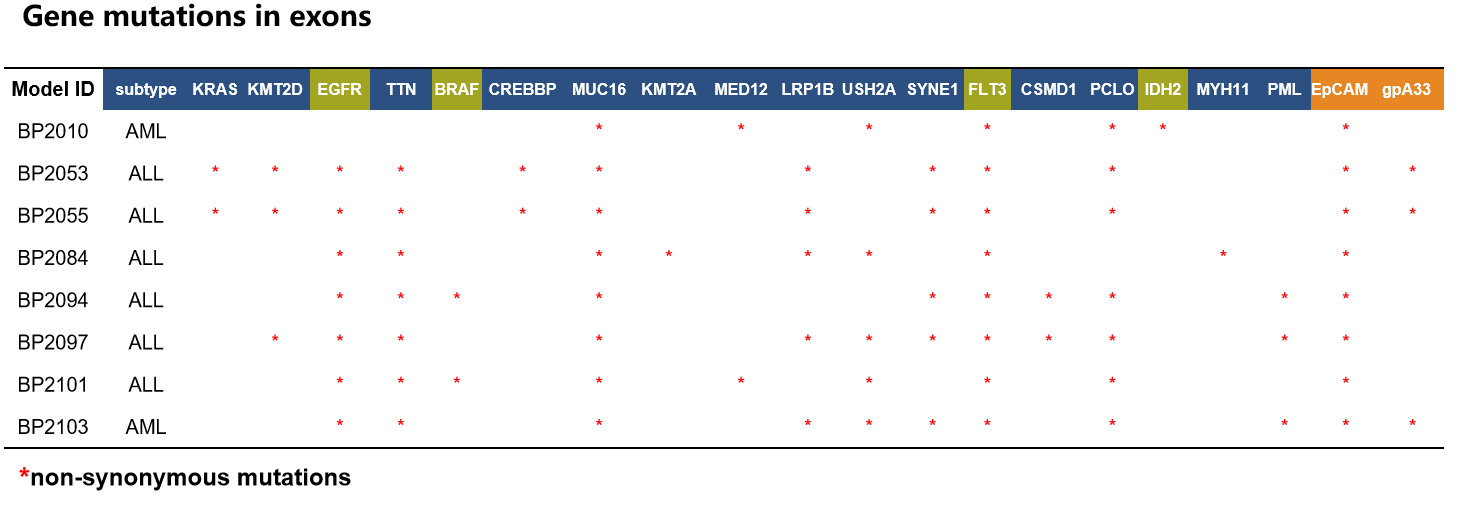
- WES(Whole Exome Sequencing) Examples
- 不同品系小鼠的生长曲线
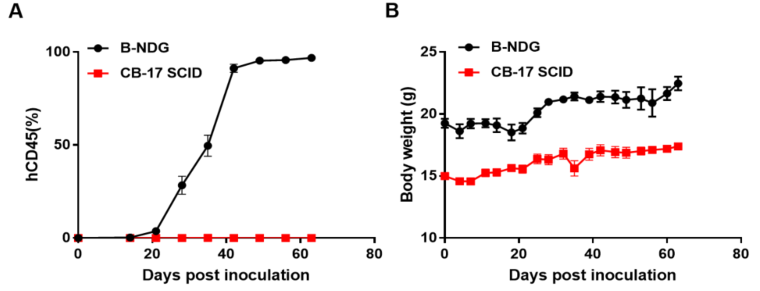
将BP2010经尾静脉接种于CB-17 SCID小鼠。每周2次测量肿瘤生长和小鼠体重,流式细胞术分析肿瘤(n=10)。(A)肿瘤平均生长速度±SEM,(B)小鼠平均体重±SEM。
结果:白血病PDX模型PDX BP2010在B- ndg中能够稳定地建立肿瘤模型,而在CB-17 SCID中不能生长。
- 化药体内疗效
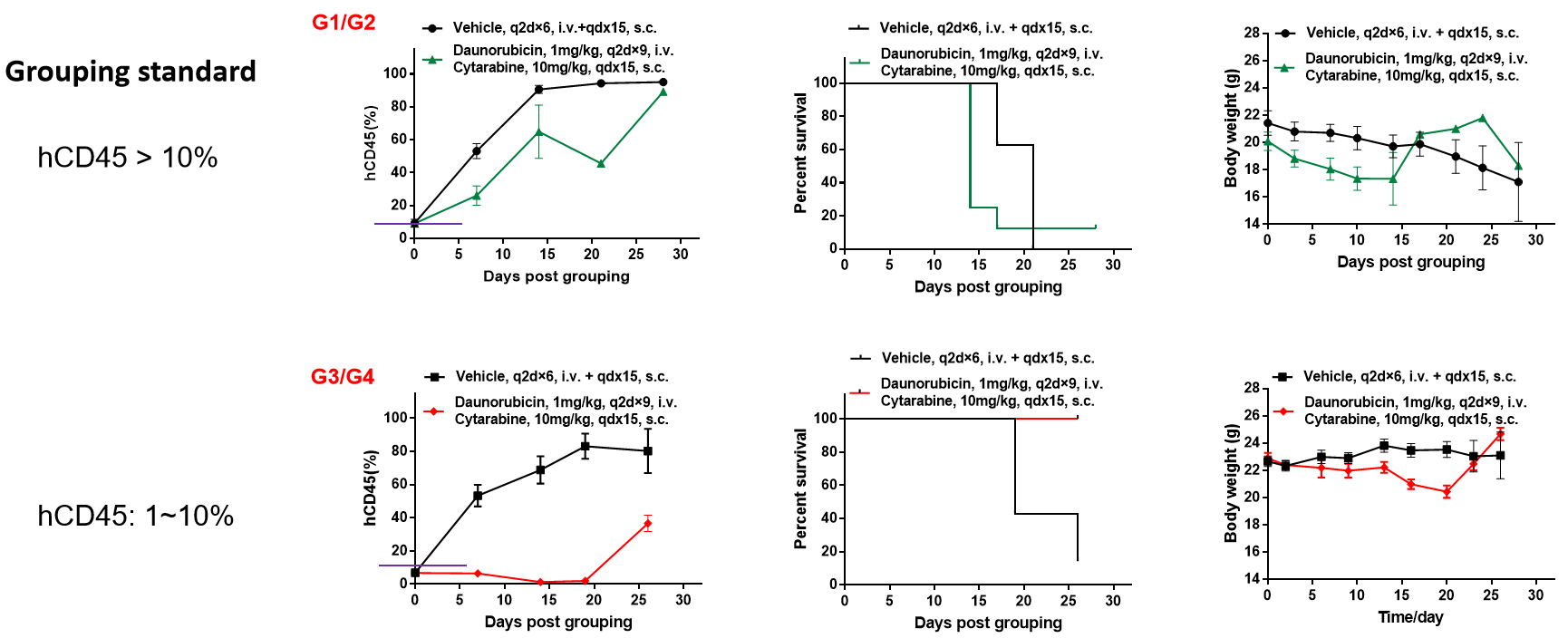
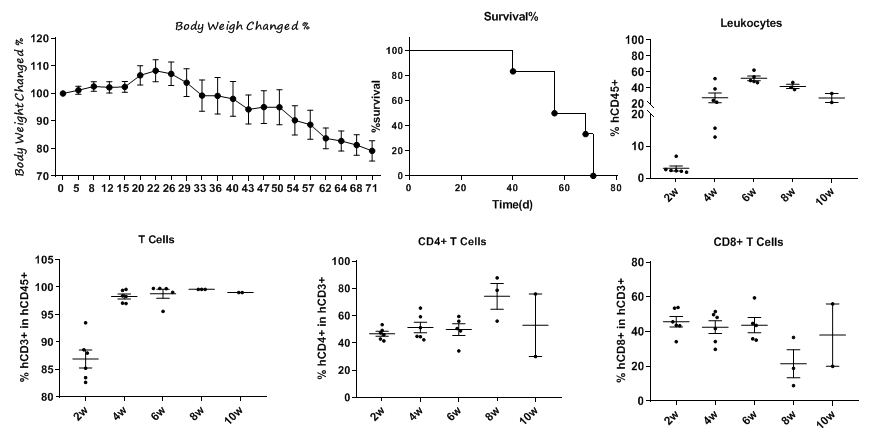
当hCD45>10%时,给药组治疗没有显著效果;当10%>hCD45>1%时,给药组抑瘤效果显著。结论:给药过程中的建模程度对小分子药物的疗效影响较大。
- 抗体药体内疗效
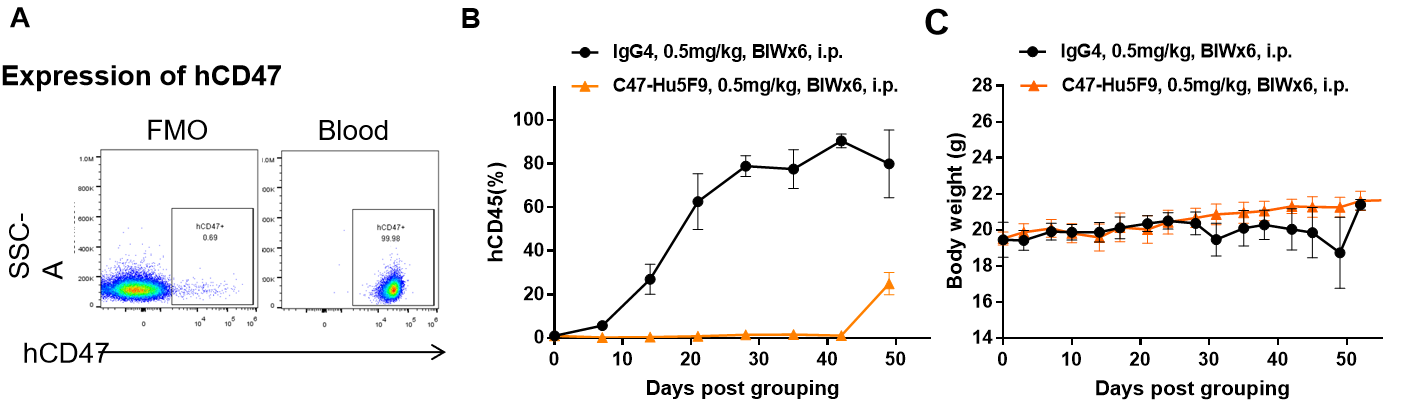
抗体在B-NDG小鼠中的抗肿瘤活性。(A)人CD47在BP2010的肿瘤细胞表面高度表达。(B)抗体CD47-Hu5F9可抑制BP2010在B-NDG小鼠中的肿瘤生长。通过尾静脉将BP2010的PDX模型接种到B-NDG小鼠(雌性,n=7)中。当小鼠外周血中的hCD45阳性细胞达到约1%时,对小鼠进行分组,此时用抗体药物和表(C)所示的方案对它们进行治疗。治疗期间体重变化。数值表示为平均值±SEM。
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn