中文
B-hSIGLEC15 MC38
|
Common name |
B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 | Catalog number | 311049 |
| Aliases | CD33L3, HsT1361, SIGLEC-15 | Disease | Colon carcinoma |
|
Organism |
Mouse |
Strain | C57BL/6 |
| Tissue types | Colon | Tissue | Colon |
模型验证
Description
The mouse Siglec15 gene was replaced by human SIGLEC15 coding sequence in B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells. Human SIGLEC15 is highly expressed on the surface of B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells.
Gene targeting strategy for B-hSIGLEC15 MC38.The partial exon 3~3’UTR of mouse Siglec15 gene were knocked out and human SIGLEC15 CDS was insert into mouse Siglec15 exon 3 in B-hSIGLEC15 MC38.
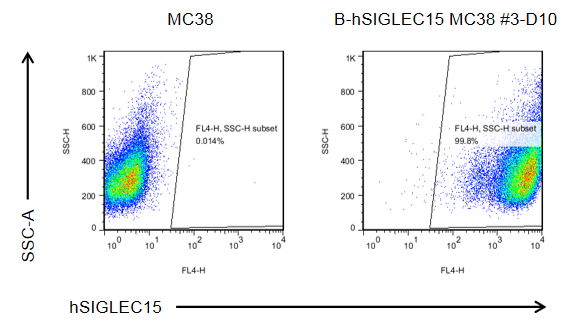
The SIGLEC15 expression analysis in B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells by flow cytometry. Single cells were collected from wild-type MC38 and B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-SIGLEC15 antibody (in house). Human SIGLEC15 was exclusively detectable in B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells but not wild-type MC38 cells. The 3-D10 clone of B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells was used for in vivo experiments.
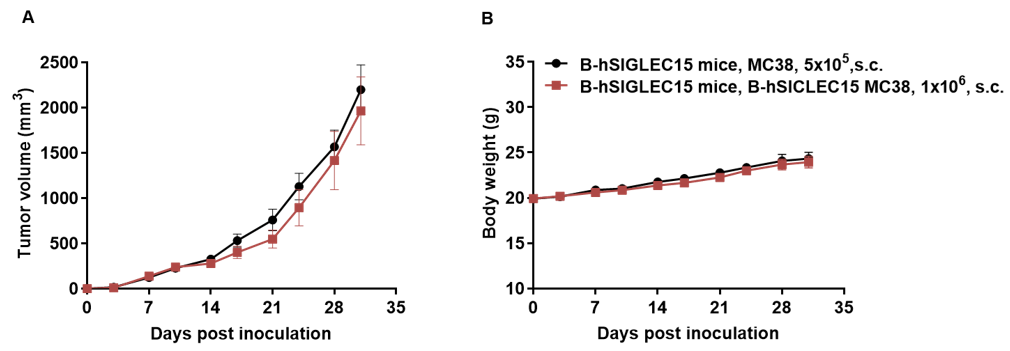
Subcutaneous homograft tumor growth of B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells. B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells (1x106) and wild-type MC38 cells (5x105 ) were subcutaneously implanted into the B-hSIGLEC15 mice (female, 8-week-old, n=6). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume ± SEM. (B) Body weight (Mean± SEM). Volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V=0.5 X long diameter X short diameter2. As shown in panel A, B-hSIGLEC15 MC38 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies.
Copyright © 2024 百奥赛图江苏基因生物技术有限公司. All Rights Reserved
备案号: 苏ICP备2021053911号-1
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn