中文
B-NDG hIL2 mice
| Strain Name |
NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen Igs2tm1(CMV-IL2)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name |
B-NDG hIL2 mice |
| Background | B-NDG | Catalog number | 113385 |
|
Related Genes |
IL-2, TCGF, lymphokine |
||
模型验证
Description
- Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a multifaceted cytokine belonging to the chemokine family. It's primarily produced by activated T cells and plays a crucial role in promoting growth, proliferation, and differentiation of lymphocytes. IL-2 has significant implications for the body's immune responses and combating viral infections. The sensitivity of different types of immune cells to IL-2 varies depending on the affinity receptors they express. IL-2 has several functions: it can activate T cells while stimulating cytokine production; it encourages NK cell proliferation, enhances their killing activity, and promotes cytokines' production; it induces LAK cell generation; stimulates B cell proliferation along with antibody secretion; and activates macrophages. Overall, IL-2 serves as an essential component in regulating immune responses.
- Gene editing strategy: The full coding sequences of human IL2 gene, including the promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR are inserted into mouse Hipp11 (H11) locus in B-NDG hIL2 mice.
- Protein expression analysis: Human IL2 was only detectable in heterozygous and homozygous B-NDG hIL2 mice but not in wild-type mice.
- Application: The B-NDG hIL12 mice serve as a valuable tool in the creation of humanized immune system models.
Protein expression analysis in serum
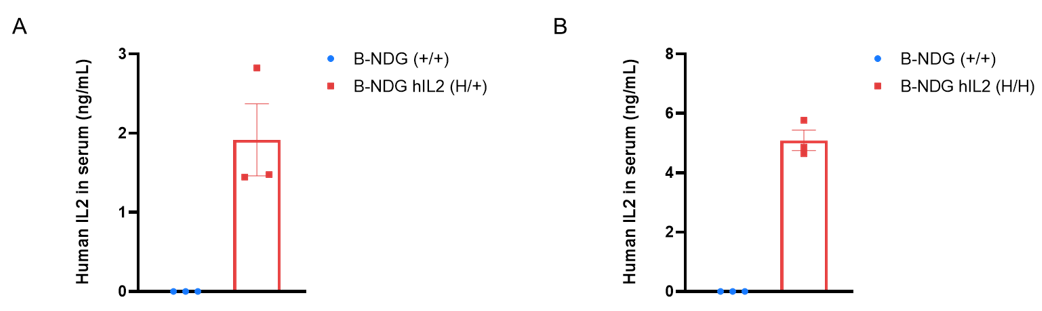
Strain specific IL2 expression analysis in heterozygous and homozygous humanized B-NDG hIL2 mice by ELISA. Serum was collected from B-NDG mice (+/+), heterozygous B-NDG hIL2 mice (H/+) and homozygous B-NDG hIL2 mice (H/H, n=3). Protein expression level of IL2 was analyzed by ELISA (anti-human IL2 antibody: Biolegend, 431804). Human IL2 was only detectable in serum from heterozygous B-NDG hIL2 mice (A) and homozygous B-NDG hIL2 mice (B), but not in wild-type mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Copyright © 2024 百奥赛图江苏基因生物技术有限公司. All Rights Reserved
备案号: 苏ICP备2021053911号-1
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680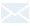 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn