Protein expression analysis

Strain specific TIGIT and PD-L1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-L1/hTIGIT mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from WT and homozygous B-hPD-L1/hTIGIT mice (H/H) mice stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo (7.5 μg/mice), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TIGIT antibody. Mouse TIGIT and PD-L1 were exclusively detected in WT mice. Human TIGIT and PD-L1 were exclusively detected in homozygous B-hPD-L1/hTIGIT mice but not WT mice.
Combination therapy of hTIGIT Ab and PD-L1 Ab
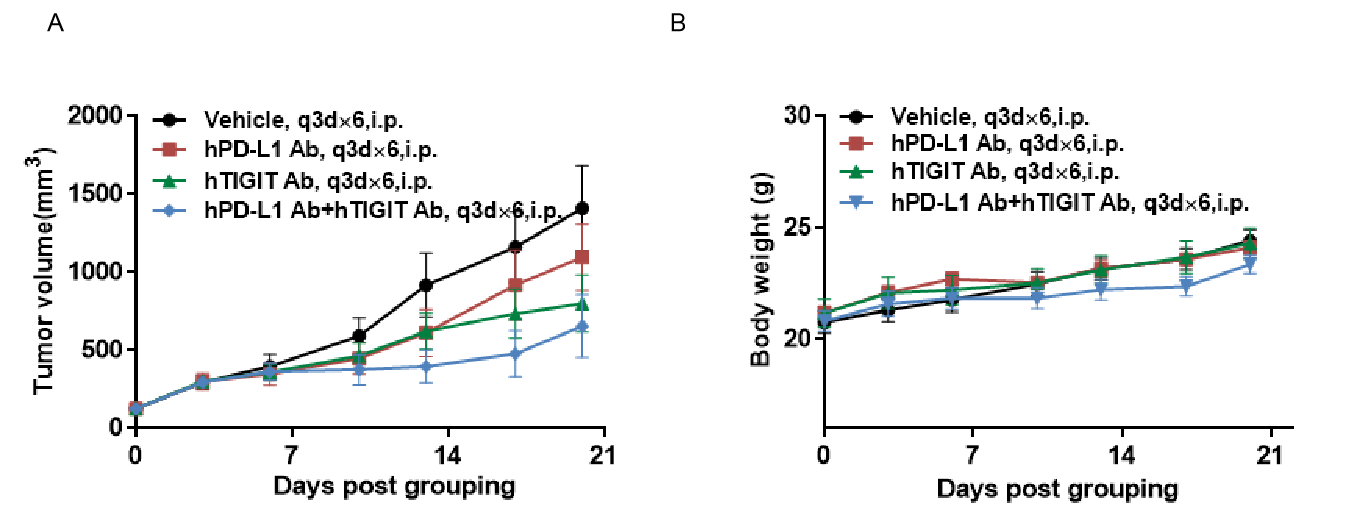
Antitumor activity of anti-hTIGIT antibody combined with anti-hPD-L1 antibody in B-hPD-L1/hTIGIT mice. (A) Anti-hTIGIT antibody combined with anti-hPD-L1 antibody inhibited MC38-hPD-L1 tumor growth in B-hPD-L1/hTIGIT mice. Murine colon cancer MC38-hPD-L1 cells (5×105) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-L1/hTIGIT mice (female, 5-8 week-old, n=7). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150±50 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-hTIGIT antibody combined with anti-hPD-L1 antibody and schedules indicated in panel (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, combination of anti-hTIGIT and anti-hPD-L1 antibody shows more inhibitory effects than individual groups, demonstrating that the B-hPD-L1/hTIGIT mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluating combination therapy efficacy of hTIGIT antibodies and hPD-L1 antibodies . Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn