中文
B-hPD-1/hGITR mice
模型验证
Protein expression analysis
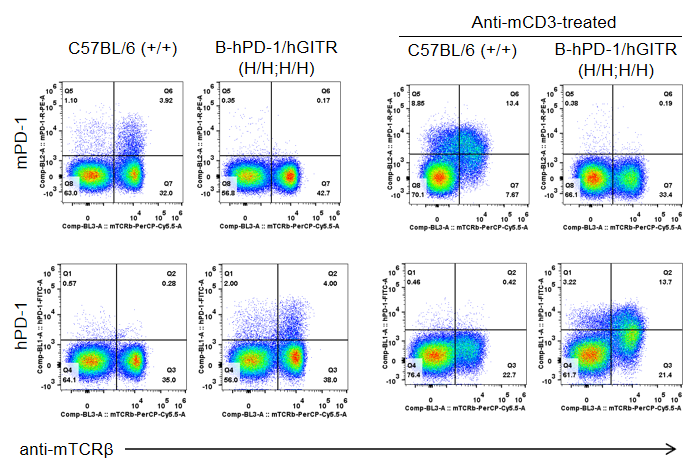
Strain specific PD-1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes from both wild type C57BL/6 (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice (H/H) were analyzed by flow cytometry. Mouse PD-1 were detectable in T cells of wild type C57BL/6 mice, while human PD-1 were only detectable in T cells of the homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice.
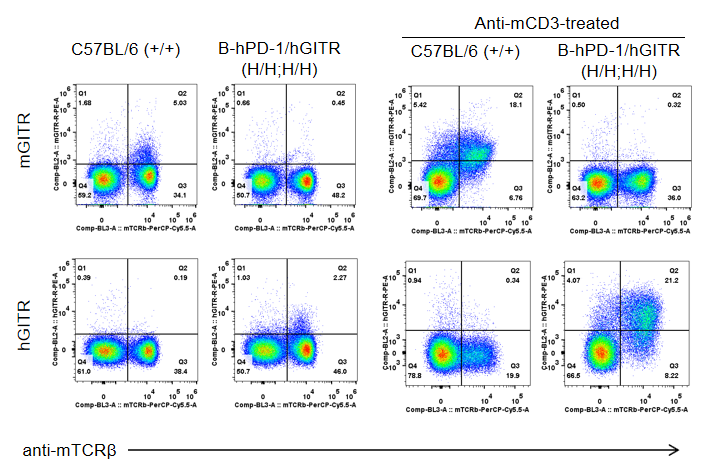
Strain specific GITR expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes from both wild type C57BL/6 (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice (H/H) were analyzed by flow cytometry. Mouse GITR were detectable in T cells of wild type C57BL/6 mice, while human GITR were only detectable in T cells of the homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice.
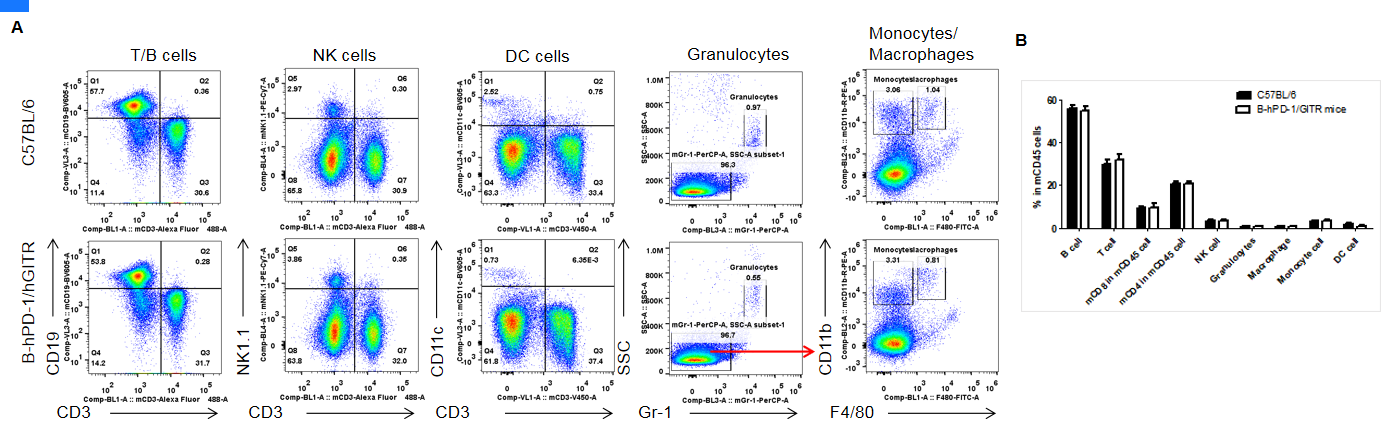
Analysis of leukocytes subpopulation in spleen. Splenocytes were isolated from C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hGITR mice (n=3). The proportion of leukocytes subpopulation was tested by flow cytometry. As a result, the expression profile of leukocytes subpopulation in homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice is similar to that in the C57BL/6 mice, indicating that differentiation of T cells, B cells, NK cells, monocytes, DC cells and macrophage cells are not affected by the humanization of hPD-1/hGITR.
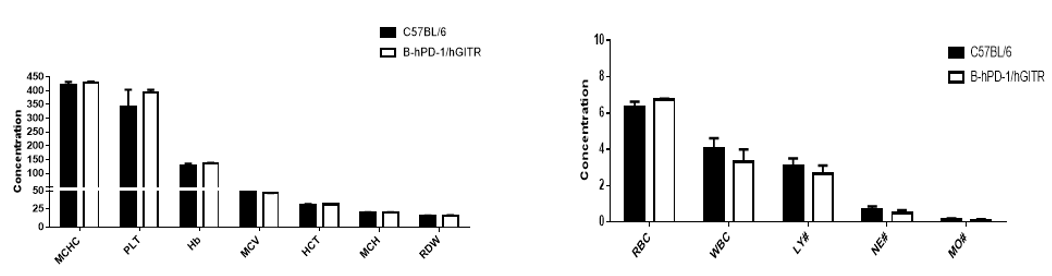
Blood Routine Test. Blood from the C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hGITR mice (n=3) was collected and analyzed by blood routine test. As a result, there is no significant differences between the C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hGITR mice.
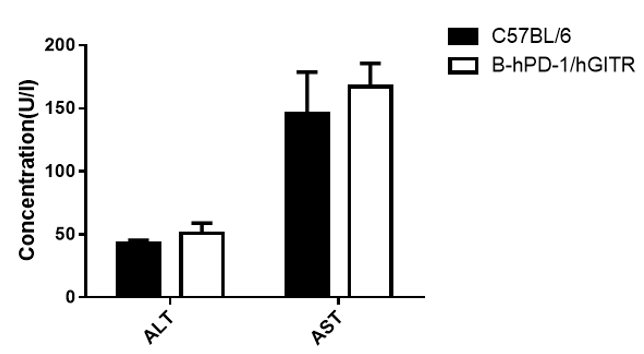
Blood chemistry tests of B-hPD-1/hGITR mice. Serum from the C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hGITR mice was analyzed for the levels of ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase). There was no differences on either measurement between C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hGITR mice, indicating that introduction of hPD-1 and hGITR in place of its mouse counterpart does not change ALT and AST levels. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
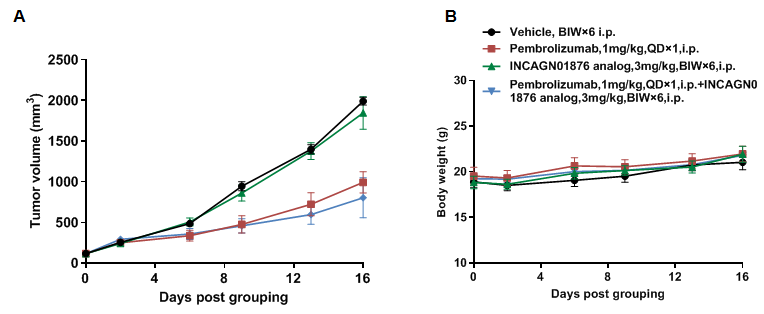
Antitumor activity of anti-GITR antibody INCAGN01876 combined with anti-hPD-1 antibody pembrolizumab in B-hPD-1/hGITR mice. (A) Anti-hGITR antibody INCAGN01876 (in house) combined with anti-hPD-1 antibodies pembrolizumab inhibited MC38-hPD-L1 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hGITR mice. Murine colon cancer MC38-hPD-L1 cells (5×105) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice (female, 7 week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100-150 mm3, at which time they were treated with antibody INCAGN01876 combined with anti-hPD-1 antibody pembrolizumab with doses and schedules indicated in panel (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, combination of anti-hGITR and anti-hPD-1 antibody shows more inhibitory effects than individual groups, demonstrating that the B-hPD-1/hGITR mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluating combination therapy efficacy of hGITR antibodies and hPD-1 antibodies . Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
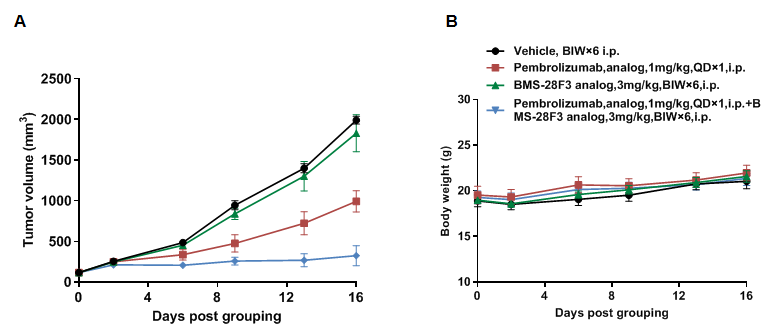
Antitumor activity of anti-GITR antibody BMS-28F3 combined with anti-hPD-1 antibody pembrolizumab in B-hPD-1/hGITR mice. (A) Anti-hGITR antibody BMS-28F3 (in house) combined with anti-hPD-1 antibodies pembrolizumab inhibited MC38-hPD-L1 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hGITR mice. Murine colon cancer MC38-hPD-L1 cells (5×105) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hGITR mice (female, 7 week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100-150 mm3, at which time they were treated with antibody BMS-28F3 (in house) combined with anti-hPD-1 antibody pembrolizumab with doses and schedules indicated in panel (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, combination of anti-hGITR and anti-hPD-1 antibody shows more inhibitory effects than individual groups, demonstrating that the B-hPD-1/hGITR mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluating combination therapy efficacy of hGITR antibodies and hPD-1 antibodies . Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Copyright © 2024 百奥赛图江苏基因生物技术有限公司. All Rights Reserved
备案号: 苏ICP备2021053911号-1
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn