mRNA and protein expression analysis
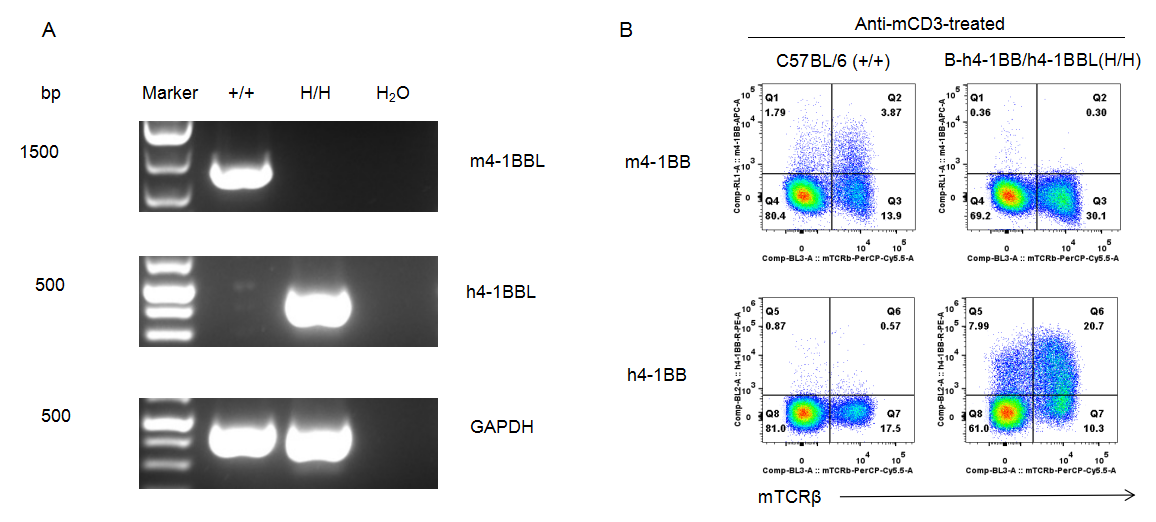
Strain specific analysis of 4-1BB and 4-1BBL gene expression in B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice by RT-PCR and FACS. (A) Mouse 4-1BBL mRNA was detectable in splenocytes of wild-type mice (+/+). Human 4-1BBL mRNA was only detectable in splenocytes of B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice (H/H) but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. (B) Mouse 4-1BB was detectable in T cells from splenocytes of wild-type mice. Human 4-1BB was detectable in T cells from splenocytes of B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice.
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice
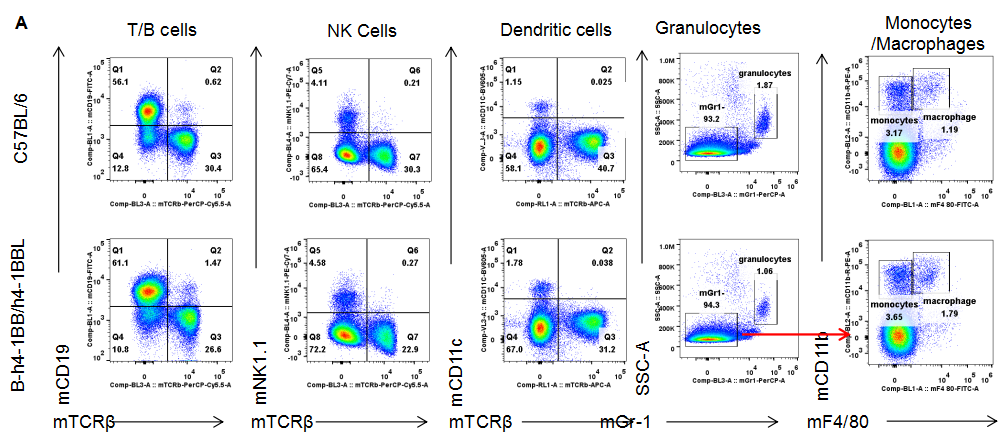

Analysis of leukocytes subpopulation in spleen. Splenocytes were isolated from C57BL/6 and B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice (n=3). The proportion of leukocytes subpopulation was tested by flow cytometry. As a result, the expression profile of leukocytes subpopulation in homozygous B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice were similar to that in the C57BL/6 mice, indicating that differentiation of T, B, NK, Monocyte, DC and macrophage cells were not affected by the humanization of B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice. The same results were observed in lymph node and blood (data was not shown).
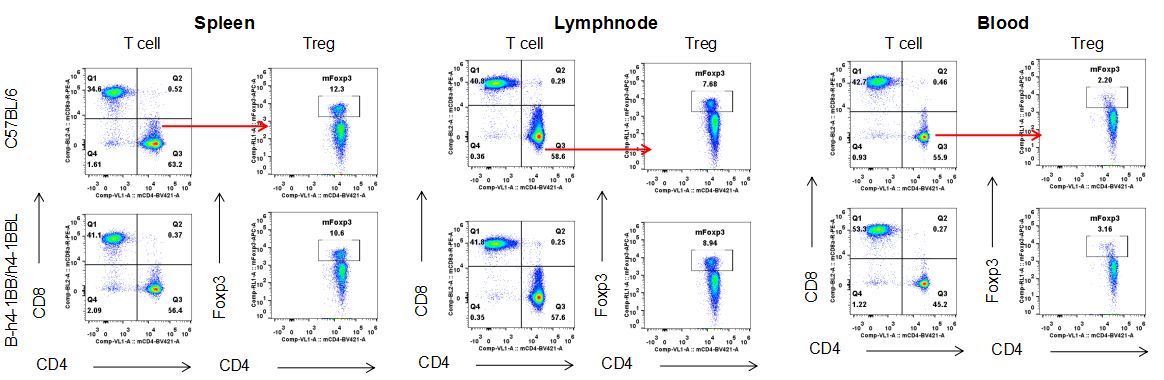
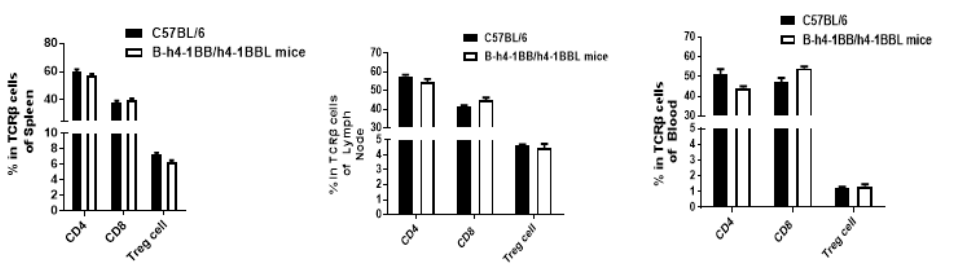
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in spleen, lymph node, blood. The lymphocytes were isolated from spleen, lymph node and blood in C57BL/6 and B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice (n=3). The proportion of T cells subpopulation was tested by flow cytometry. There were no differences between wild-type and B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice.
High-dose of Urelumab resulted in liver toxicity both in B-h4-1BB mice and B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice
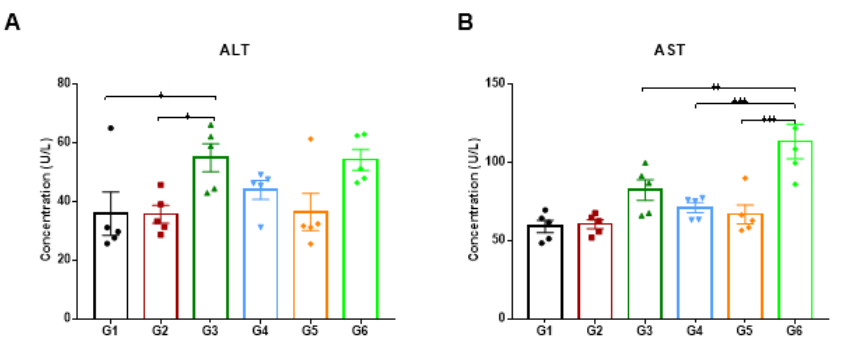
High-dose human 4-1BB antibody Urelumab caused liver toxicity in B-h4-1BB mice and B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice. Homozygous B-h4-1BB mice and B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice were treated with PBS or Urelumab (in house) as indicated on the graph (n=5, female, 7-week-old). Serum was collected and detected the ALT and AST on day 21. Urelumab at 20 mg/kg caused significant increase of ALT compared with PBS control in B-h4-1BB mice, while the same treatment had no effect in B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice. On the contrary, there was no significant increase of AST compared with PBS control in B-h4-1BB mice, but 20ug/mL urelumab treatment caused a significant increase of AST in B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice. There was no significant change in ALT and AST in the 1mg/kg dose group both in B-h4-1BB mice and B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
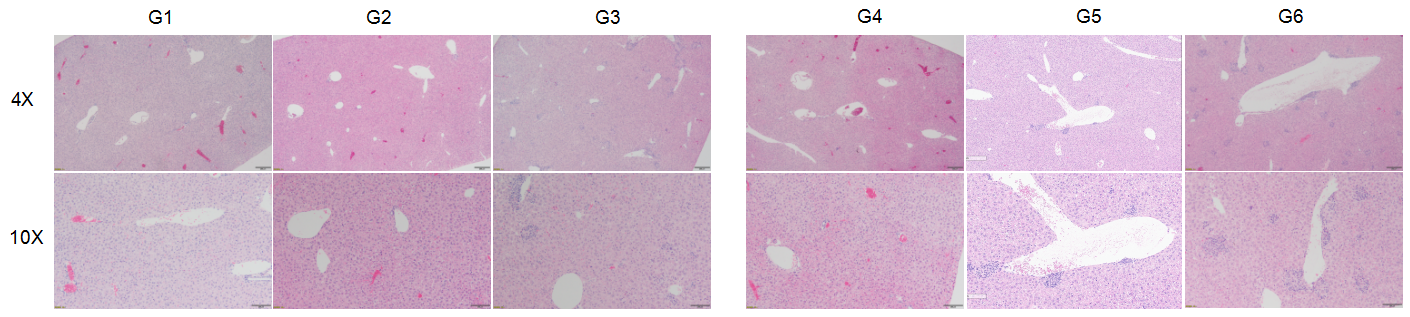
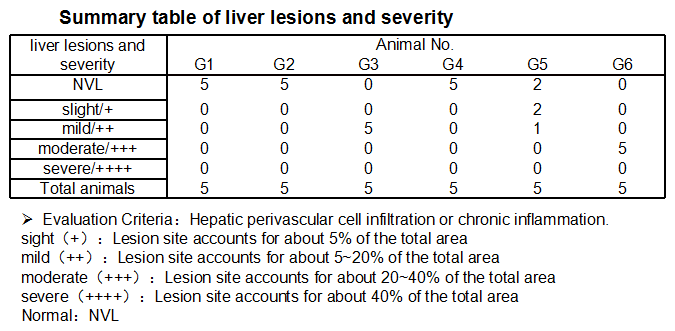
- In B-h4-1BB Mice (G1-G3), no obvious abnormal changes were observed in the liver when the urelumab dose was 1mg/kg (G2). At a dose of 20 mg/kg (G3) changes were observed in 5/5 of the animals, manifested as perivascular cell infiltration or chronic inflammation in the liver, with mild lesions.
- In B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice (G4-G6), 1 mg/kg group(G5) 3/5 of mice show pathological changes(slight 2/5, mild 1/5), but in 20 mg/kg dose (G6), all of the experimental animals could see moderate changes in liver (5/5) . Overall, the degree and incidence of liver lesions in the 20 mg/kg group (G6) were significantly higher than that in the 1 mg/kg group (G5).
- The above results suggested that urelumab at 20 mg/kg was more likely to perivascular cell infiltration or chronic inflammation in the liver than that at 1 mg/kg. B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice were more sensitive to urelumab toxicity effects than B-h4-1BB mice.
- B-h4-1BB/h4-1BBL mice was a good preclinical toxicity evaluation model.
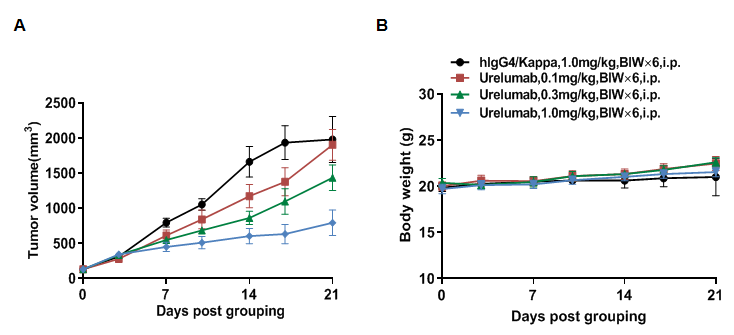
In vivo efficacy of anti-4-1BB antibodies
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn