| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-Gcgrtm1(GCGR)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hGCGR mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number | 110105 |
|
Aliases |
GGR, GL-R,G, GR | ||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
14527 | ||
mRNA expression analysis


Species specific analysis of GCGR gene expression in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and homozygous B-hGCGR mice by RT-qPCR. Organs were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and homozygous B-hGCGR mice (7-8 weeks old, 2 male and 2 female in each group). Primer sequences were designed in the conserved sequences between human GCGR and mouse Gcgr genes. The expression levels of GCGR mRNA in liver and kidney of wild-type mice and B-hGCGR mice are relatively higher compared to other organs. The mRNA expression levels of GCGR in B-hGCGR mice are similar to those in the wild-type mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
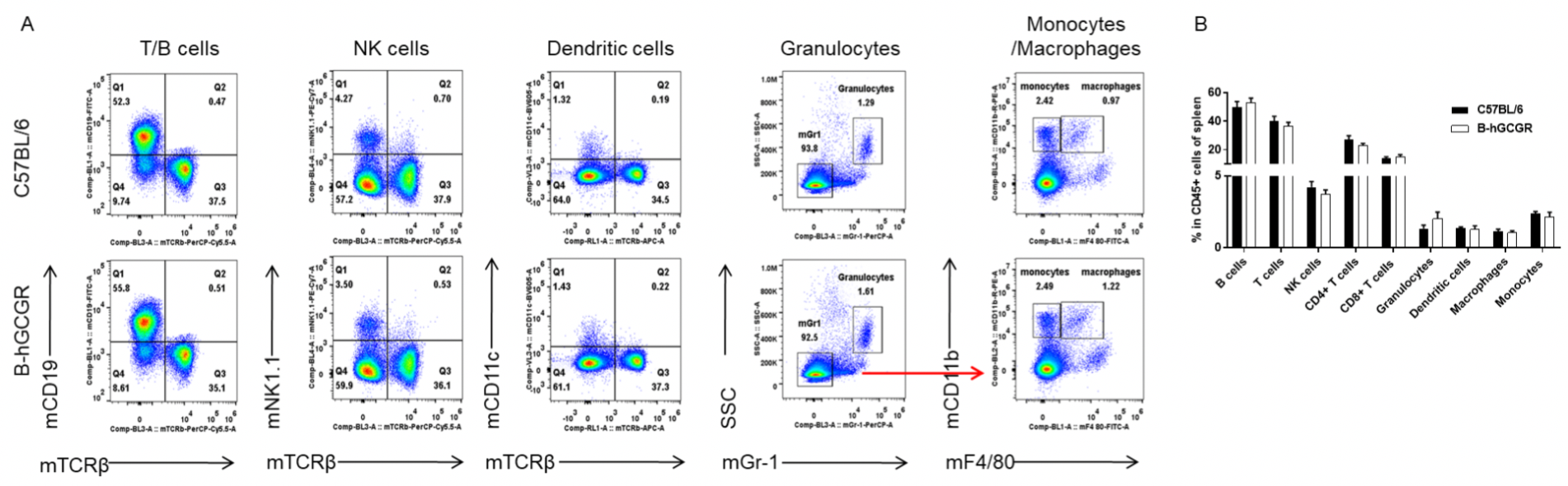
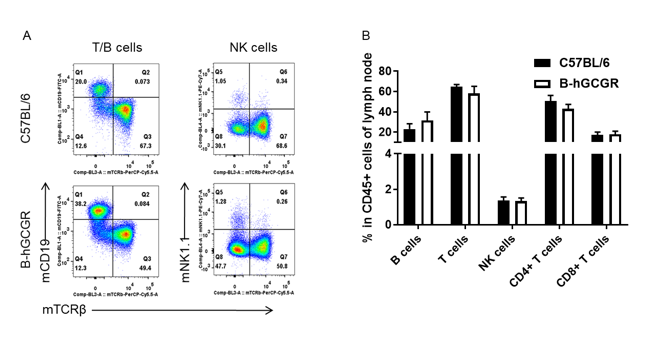

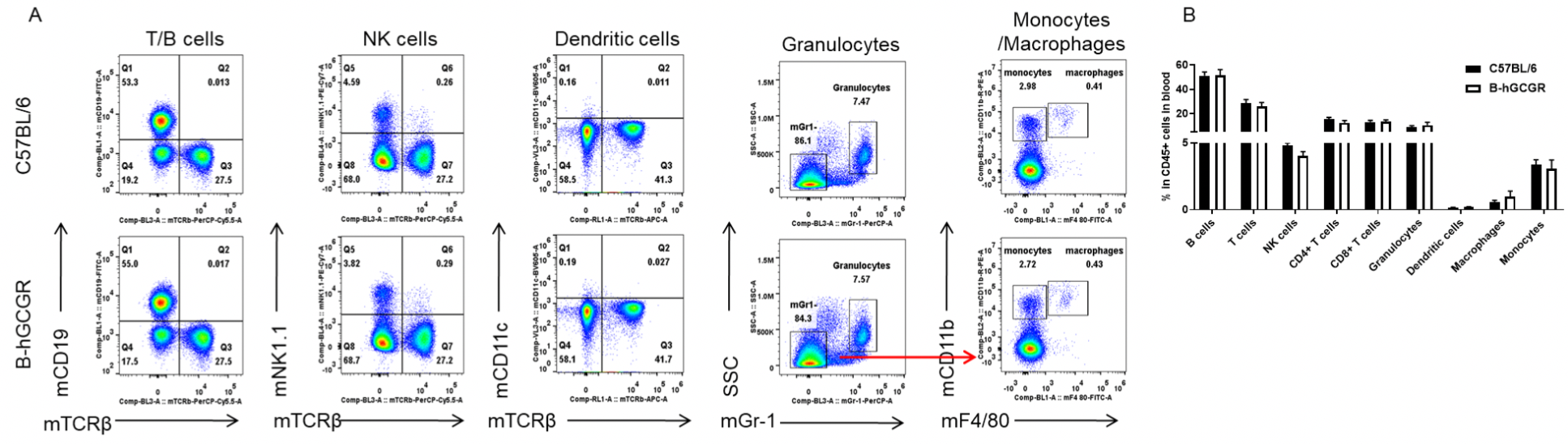
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in B-hGCGR mice
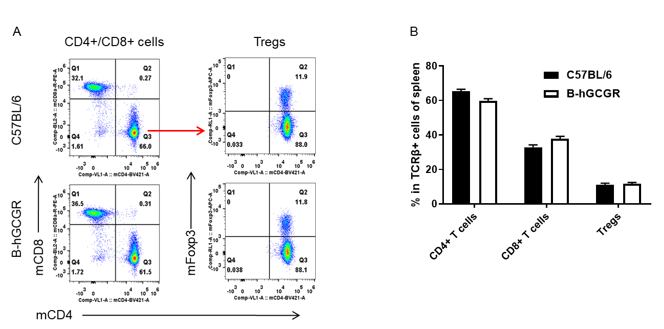
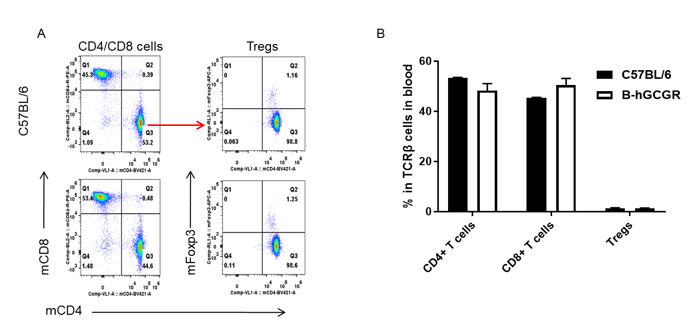
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in B-hGCGR mice
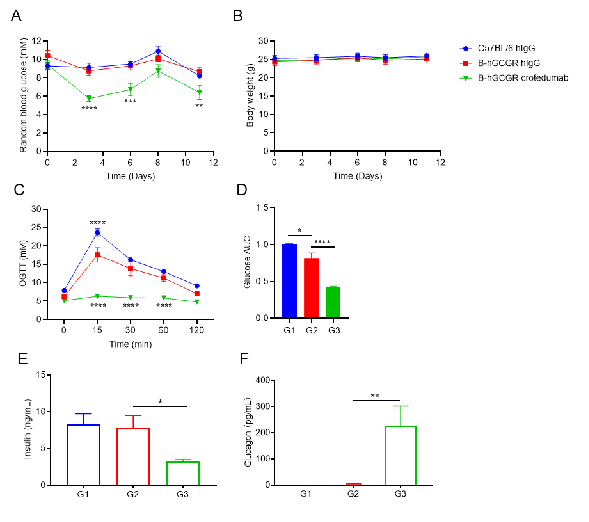
In vivo efficacy of anti-human GCGR antibody with B-hGCGR mice
In vivo efficacy of anti-human GCGR antibody with B-hGCGR mice
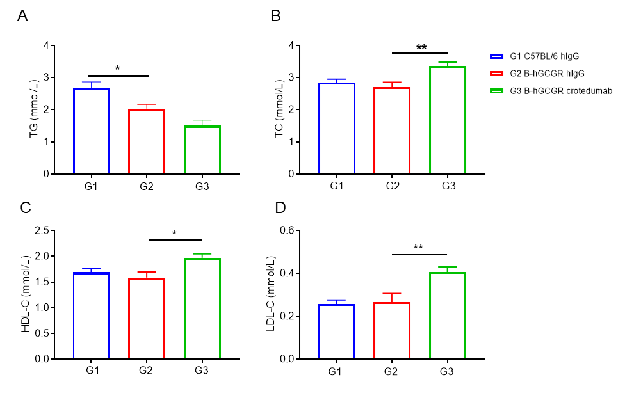
Wild-type C57BL/6 and B-hGCGR mice were treated with crotedumab (in house) or isotype control antibody (n = 6). Blood were collected on Day 11 for triglycerides and cholesterol analysis. Serum levels of TG (A) and TC (B). HDL-C (C) and LDL-C (D) levels in serum. Serum levels of TG was reduced, while TC, HDL-C and LDL-C were increased in the anti-human GCGR antibody treated male mice group compared to the isotype control. All of the results in B-hGCGR mice were similar to those in the wild-type C57BL/6. Results indicated that lipid metabolism in humanized B-hGCGR mice was similar to the wild-type C57BL/6. Results indicated that anti-human GCGR antibody was efficacious in controlling blood lipid in male B-hGCGR mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. TG, triglycerides; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human GCGR antibody with diet-induced obese (DIO) B-hGCGR mice
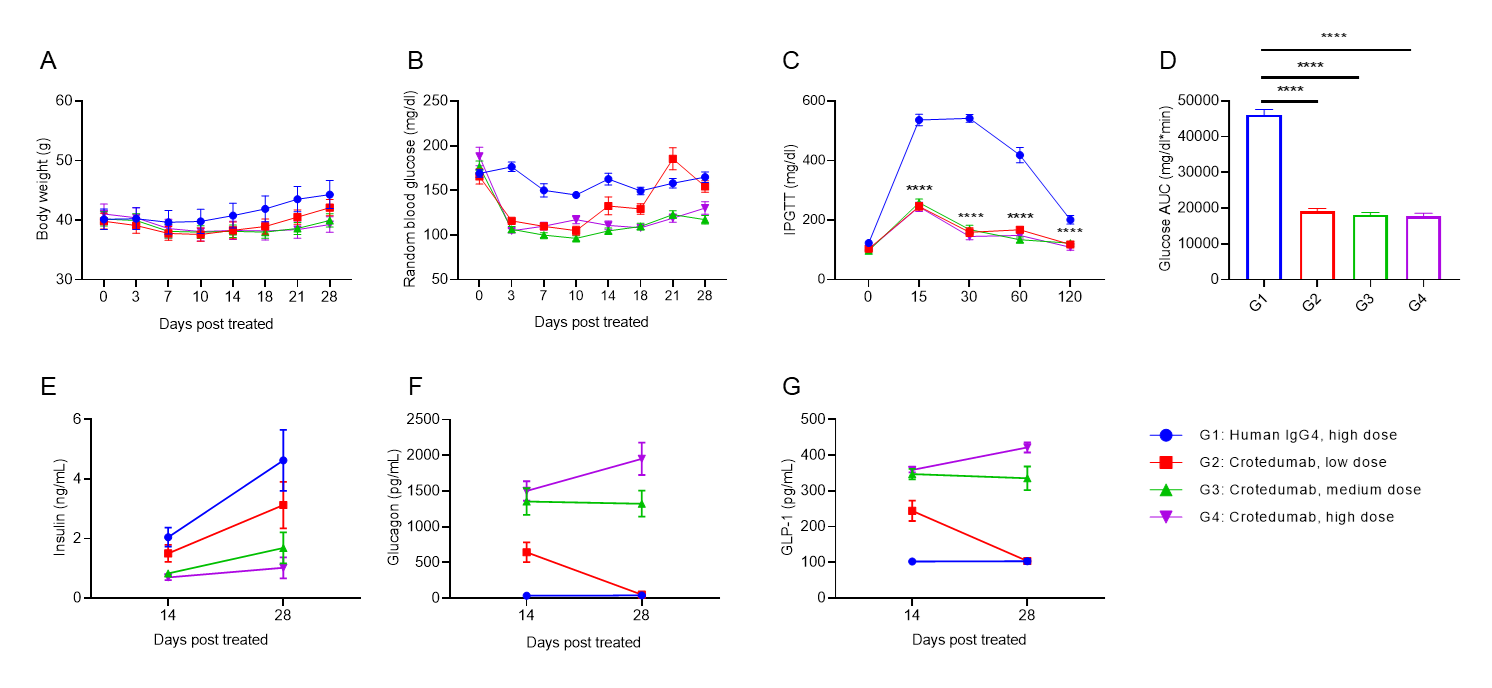
Anti-human GCGR antibody reduces blood glucose in DIO B-hGCGR mice. Male B-hGCGR mice were fed with high-fat diet throughout the study. Anti-human GCGR antibody crotedumab (in house) was administered by intraperitoneal injection on day 0 after diet-induced. Body weights, levels of blood glucose and hormones were measured periodically (n = 10). A. Body weights. B. Random blood glucose from male mice before and at multiple time points after injection of crotedumab (in house) or isotype antibody. C. IPGTT on day 5. D. Area under the curve for the IPGTT shown in C. Serum levels of (E) insulin, (F) glucagon, (G) GLP-1 on Day 14 and Day 28. Anti-GCGR antibody significantly reduced body weight, random blood glucose and IPGTT compared to the isotype control in male DIO B-hGCGR mice. Serum levels of insulin, glucagon and GLP-1 were changed with dose-dependent. Results indicated that anti-human GCGR antibody was efficacious in controlling body weight and blood glucose in B-hGCGR mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. IPGTT, Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test.
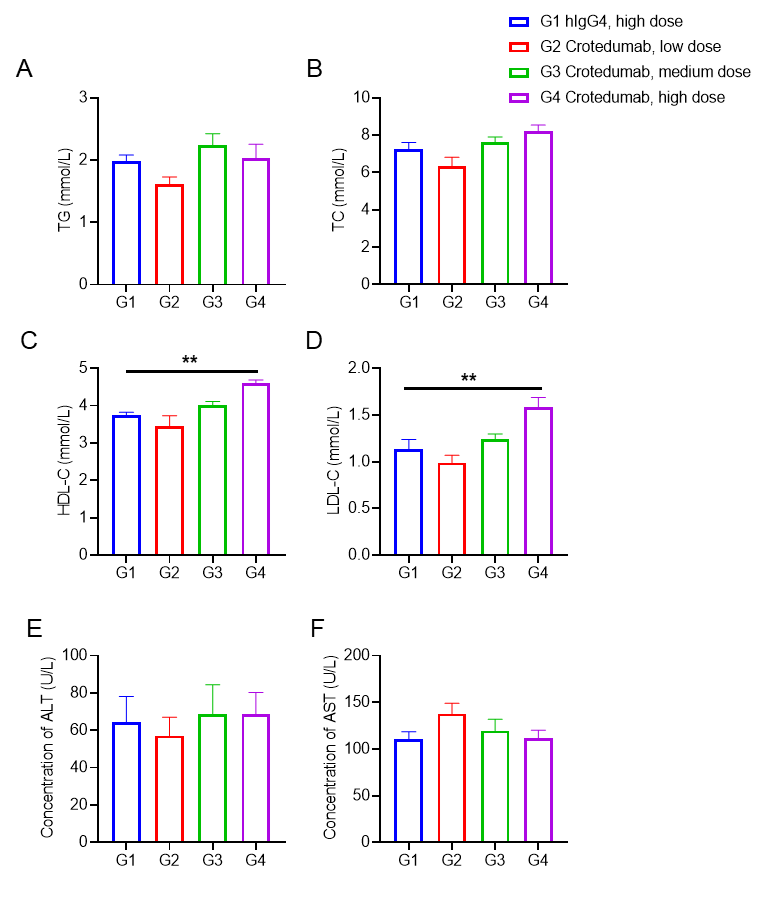
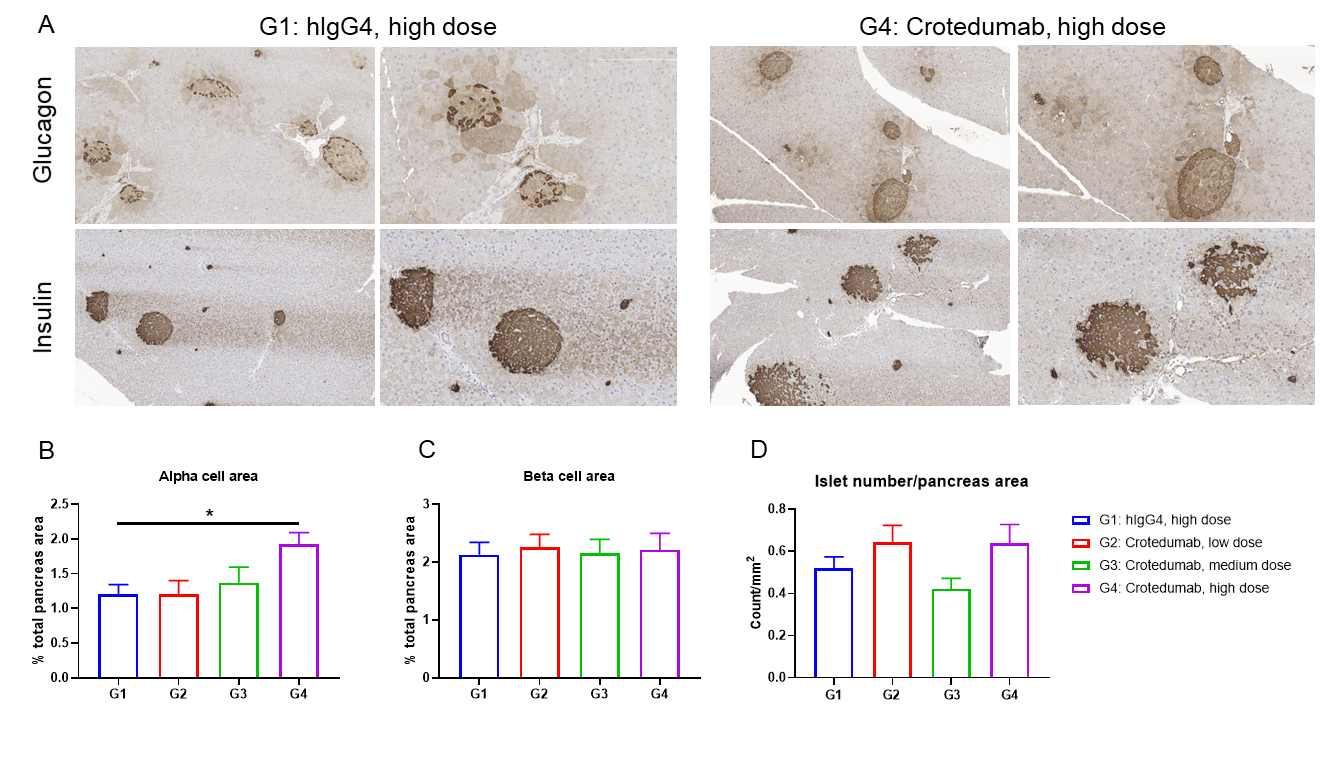
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn