| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-Il17atm1(IL17A)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hIL17A mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number |
110053 |
|
Aliases |
IL17A, CTLA-8, CTLA8, IL-17, IL-17A, IL17, ILA17, interleukin 17A | ||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
16171 | ||
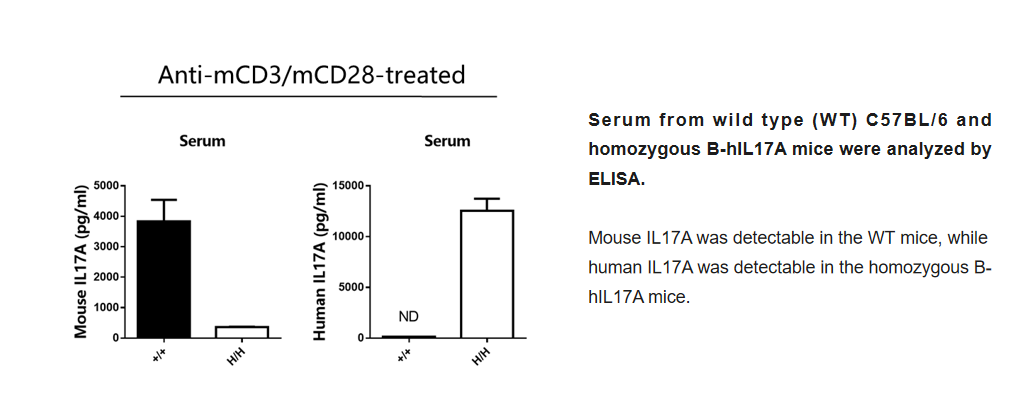
Protein Expression Analysis
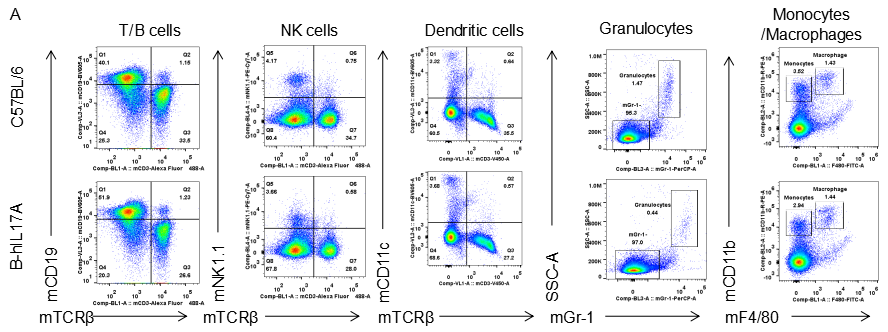
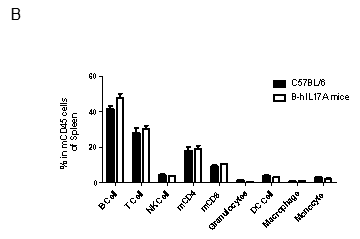
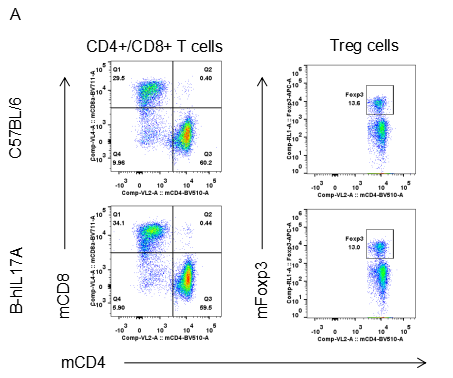
Analysis of spleen leukocytes cell subpopulations in B-hIL17A mice
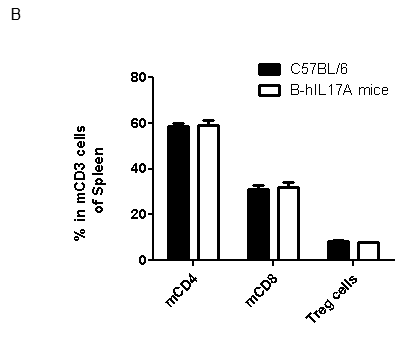
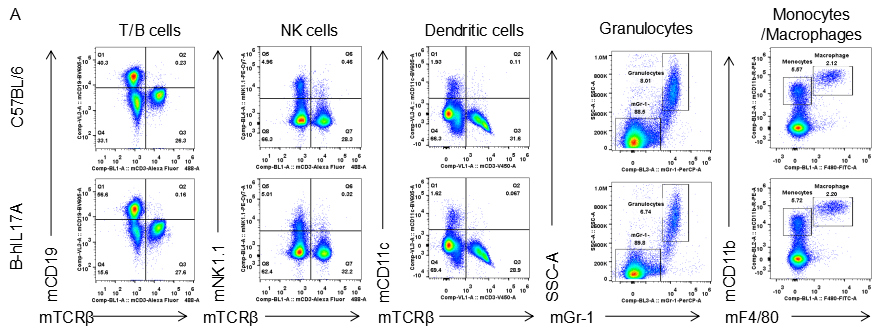

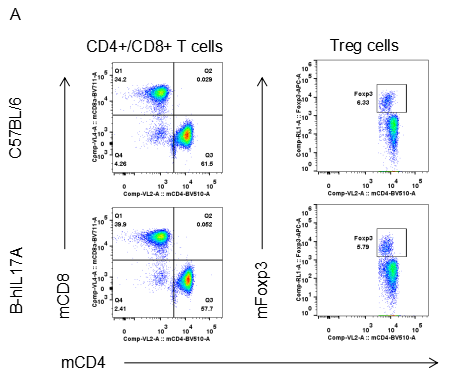
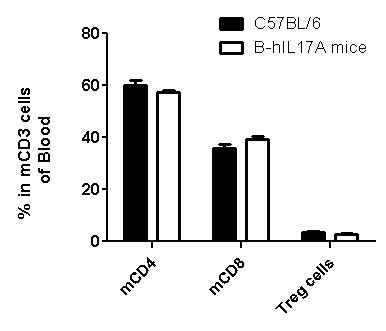
Blood routine test in B-hIL17A mice
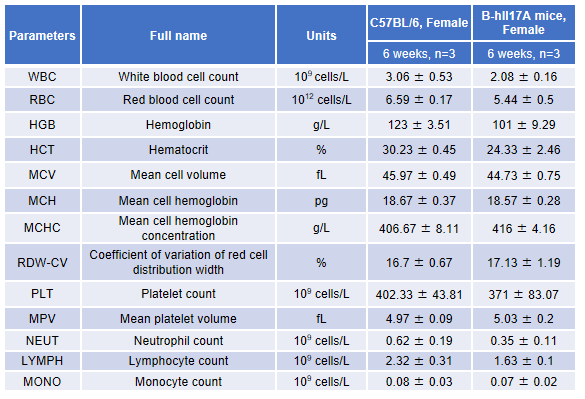
Blood from female C57BL/6 and B-hIL17A mice (n=3, 6 week-old) was collected and analyzed for CBC. There was no differences among any measurement between C57BL/6 and B-hIL17A mice, indicating that introduction of hIL17A in place of its mouse counterpart does not change blood cell composition and morphology. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
MS/EAE model
Schematic of EAE model
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an induced demyelinating disease model that closely resembles the progression and symptoms of the human neurological disease Multiple Sclerosis (MS).

Clinical score of EAE model
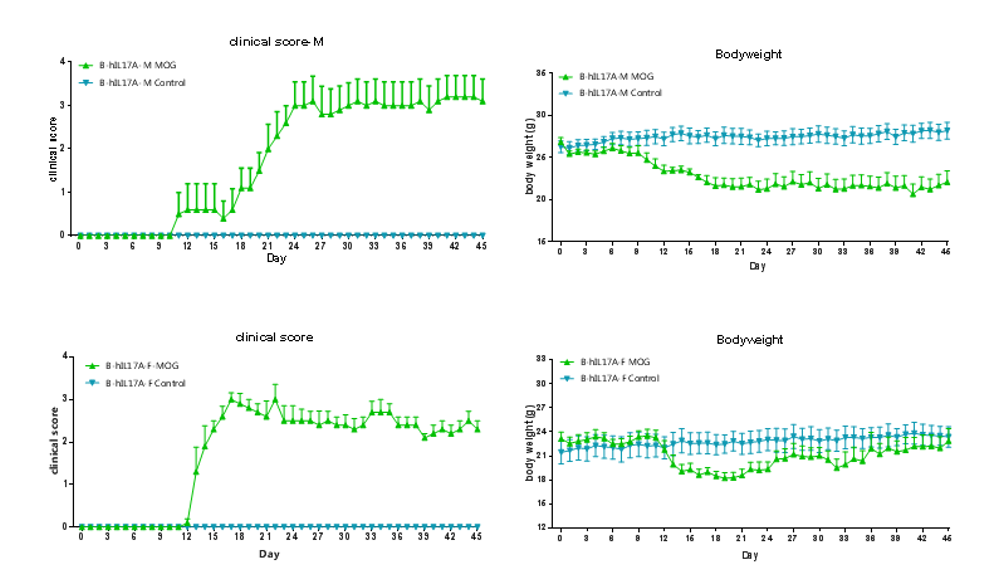
EAE induction by MOG35–55/CFA Emulsion PTX in 10-week-old B-hIL17A mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from a typical experiment (n = 5 except n = 4 for B-hIL17A-F PBS). MOG: myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein; PTX: pertussis toxin. F: female; M: male.
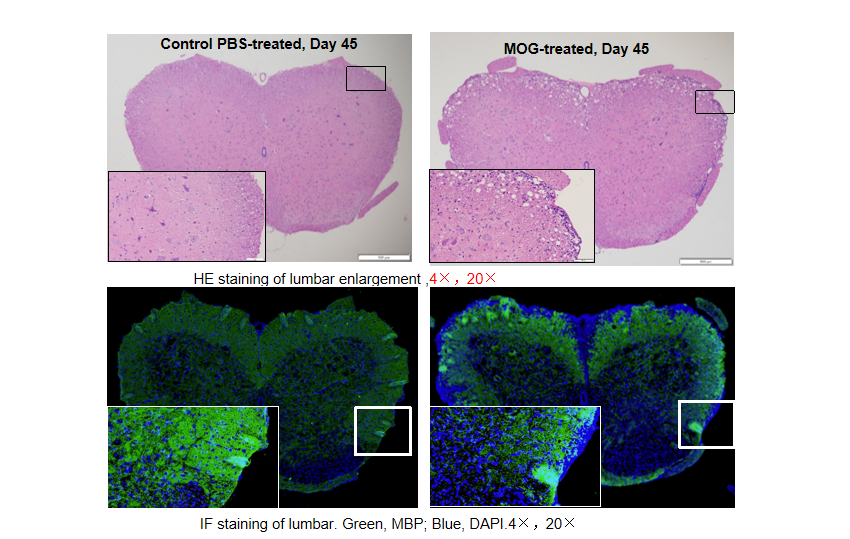
Local inflammation of the CNS in B-hIL17A mice (female,n=5) during EAE. On day 45 after MOG/CFA and PTx immunization, spinal cords were removed. The tissue sections were stained with H&E(A,B) and IHC (C,D)(Green, MBP; Blue, DAPI). The sections at the lumbar level are shown. The results showed that the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the MOG group was significantly increased, and the myelin protein was greatly reduced.
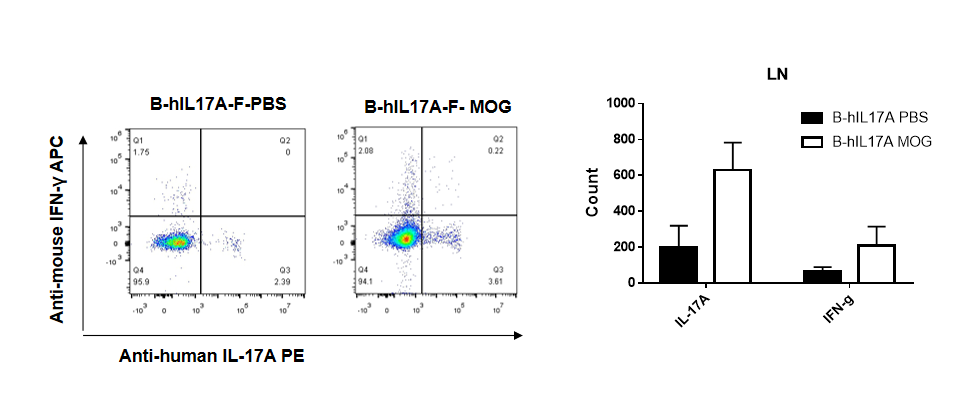
IL-17 was primarily produced by CD4 Th17 cells during the development of EAE. To detect IL-17 production, cells from lymph node of B-hIL17A mice(female,n=5) immunized with MOG/CFA were stimulated for 6 hours by PMA and ionomycin in the presence of brefeldin A. IL-17-producing cells were analyzed by FACS, along with IFNg. The percentage of IL-17+CD3+CD4+ T cells in CD3+CD4+ T cells was increased in response to MOG immunization in B-hIL17A mice (left panel). So was percentage of IFNg+ T cells.
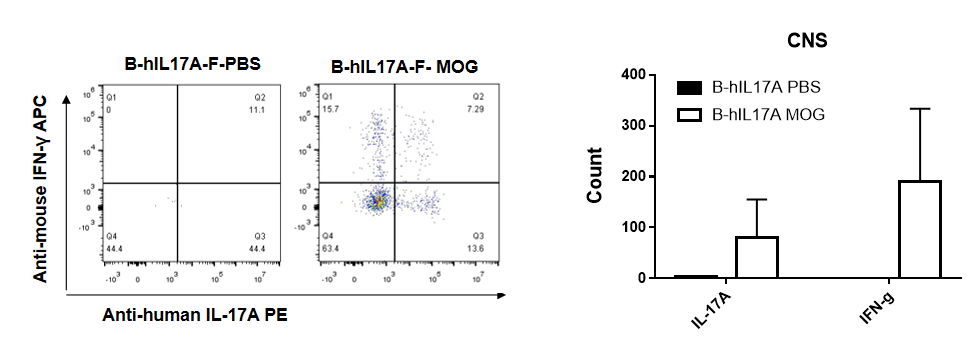
IL-17 was primarily produced by CD4 Th17 cells during the development of EAE. To detect IL-17 production, cells from CNS(Brain cell) of B-hIL17A mice(female,n=5) immunized with MOG/CFA were stimulated for 6 hours by PMA and ionomycin in the presence of brefeldin A. IL-17-producing cells were analyzed by FACS, along with IFNg. The percentage of IL-17+CD3+CD4+ T cells in CD3+CD4+ T cells was increased in response to MOG immunization in B-hIL17A mice (left panel). So was percentage of IFNg+ T cells.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human IL17A antibodies in EAE model of B-hIL17A mice

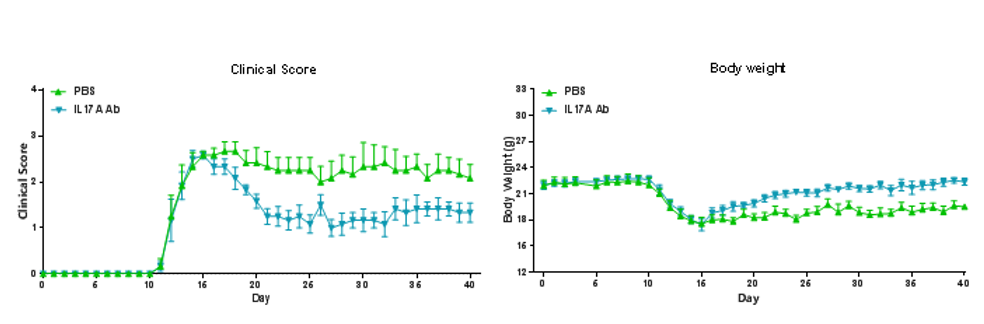
EAE induction by MOG35–55/CFA Emulsion PTX in B-hIL17A mice. The clinical score and body weight was collected after the treatment of anti-hIL17A antibody. After treatment of anti-hIL17A antibody, the clinical score level was much lower than the control in homozygous B-hIL17A mice.Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from a typical experiment (n = 6). MOG: myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein; PTX: pertussis toxin.

In vivo efficacy of anti-human IL17A antibodies in psoriasis model induced in B-hIL17A mice
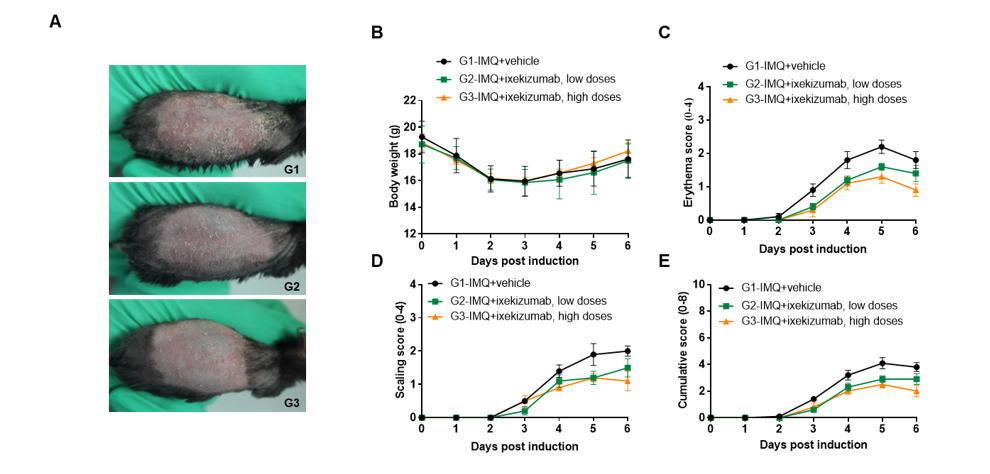
IMQ-induced skin inflammation in B-hIL17A mice phenotypically resembles psoriasis. Mice (female, 10 week-old, n=5) were scored daily for up to 6 days for body weight and clinical signs of skin inflammation following treatment with imiquimod (IMQ) cream. Mice in each group were treated with different dose of ixekizumab produced in house. Doses are shown in legend. (A) Phenotypical presentation of mouse back skin after 6 days of treatment. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. (C-D) Erythema and scaling score of the back was scored daily on a scale from 0 to 4. Additionally, the cumulative score (erythema plus scaling) is depicted. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
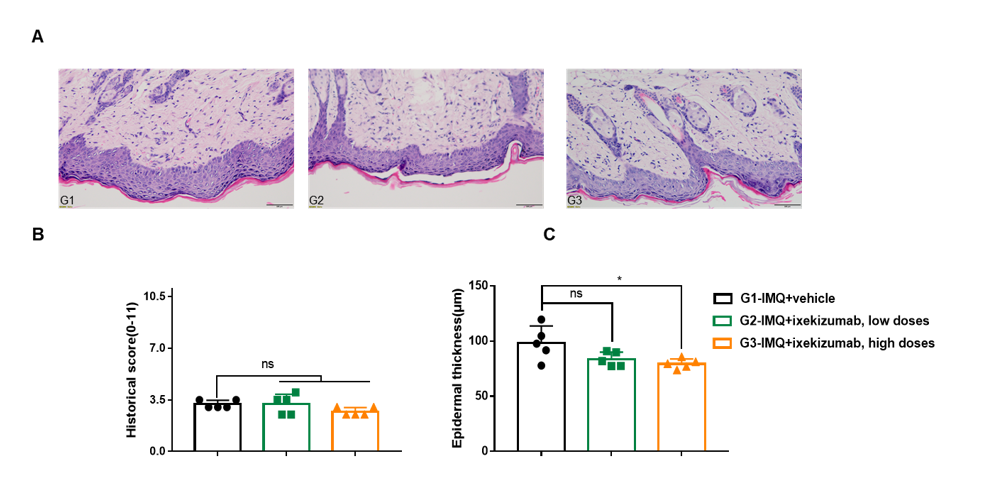
Dose dependent effects of BsAbs on keratinocyte proliferation and inflammatory cell infiltration in IMQ induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in B-hIL17A mice. Back skin was collected at the endpoint and stained with Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). (A) H&E staining of the back skin. (B) Epidermal thickness of the mice. (C) Histological changes were scored on a scale from 0 to 11. Results indicated that therapeutic effects of ixekizumab (in house) on psoriasis-like skin lesions in B-hIL17A mice were dose dependent, confirming that B-hIL17A mice provide a powerful model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human IL17A bispecific antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human IL17A antibodies in psoriasis model induced in B-hIL17A mice
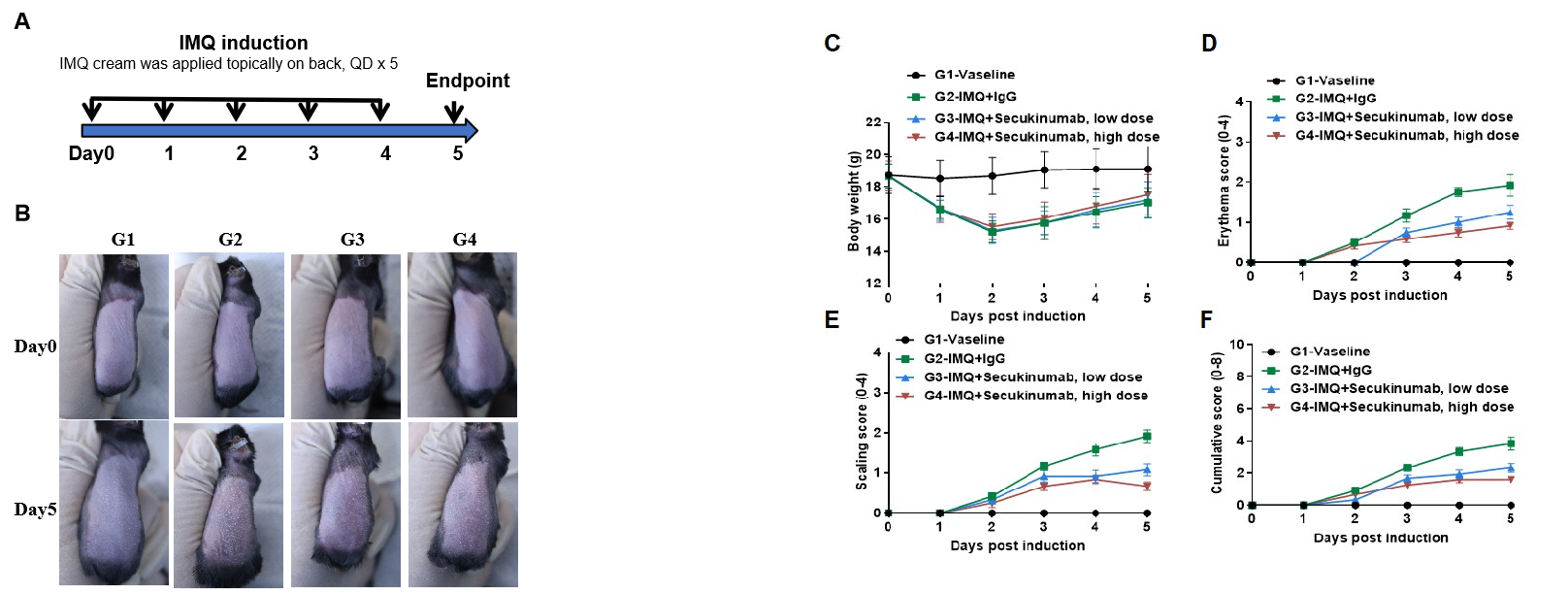
IMQ-induced skin inflammation in B-hIL17A mice phenotypically resembles psoriasis. Mice (female, 8 week-old, n=6) were scored daily for up to 6 days for body weight and clinical signs of skin inflammation following treatment with imiquimod (IMQ) cream. Mice in each group were treated with different doses of Secukinumab (commercial drug). (A) Experimental schedule for induction of psoriasis-like skin lesions in B-hIL17A mice. (B) Phenotypical presentation of mouse back skin at day0 and day 5. (C) Body weight changes during treatment. (D-E) Erythema and scaling score of the back was scored daily. Additionally, the cumulative score (erythema plus scaling) is depicted. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human IL17A antibodies in psoriasis model induced in B-hIL17A mice
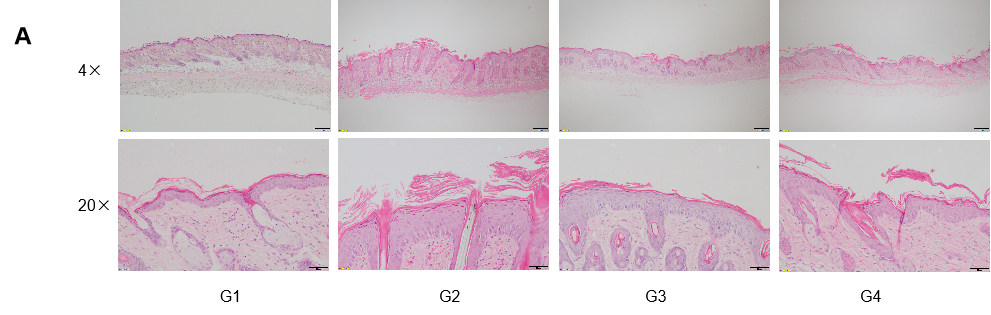
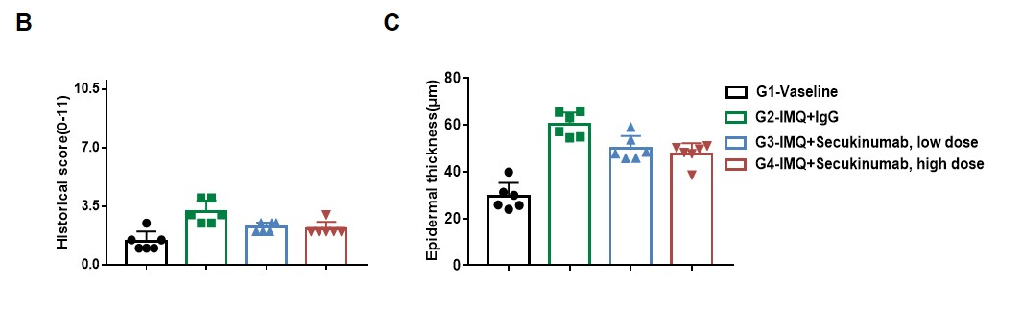
Dose dependent effects of antibodies on keratinocyte proliferation and inflammatory cell infiltration in IMQ induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in B-hIL17A mice. Back skin was collected at the endpoint and stained with Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). (A) H&E staining of the back skin. (B) Histological changes were scored. (C) Epidermal thickness of the mice. Results indicated that therapeutic effects of Secukinumab (commercial drug) on psoriasis-like skin lesions in B-hIL17A mice were dose dependent, confirming that B-hIL17A mice provide a powerful model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human IL17A antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
 苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技
苏公网安备:32068402320845号
网站建设:北京分形科技






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn